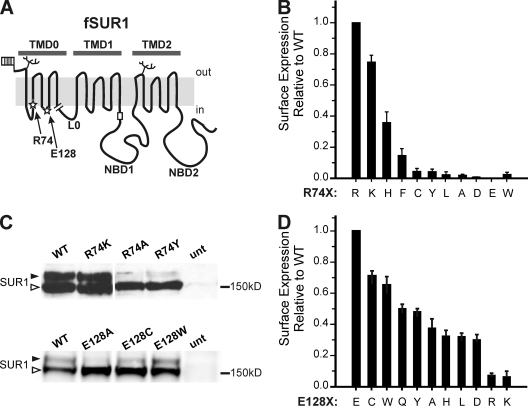
Figure 1.
Expression studies of fSUR1 R74X and E128X KATP channels. (A) Schematic of fSUR1 structure including topological domains and the placement of residues R74 and E128 (stars), glycosylation sites (branches), extracellular FLAG epitope (flag), and the RKR–ER-retention motif (rectangle). The end of the TMD0 (amino acid 198) construct used in subsequent experiments is shown by the break. (B) Chemiluminescence assays were performed to quantitatively assess how surface expression of KATP channels is affected by different amino acids at position 74 of SUR1. Surface expression is shown relative to WT channel expression. Error bars represent SEM; n = 3–6 for each condition. (C) Representative immunoblots using anti-SUR1 antibody to detect expression of fSUR1 protein in cells cotransfected with Kir6.2 and either fSUR1 R74X (top) or E128X (bottom) cDNAs. SUR1 protein undergoes differential glycosylation, such that core-glycosylated protein (bottom band, open arrow head) becomes complex glycosylated (top band, filled arrow head) upon trafficking through the Golgi; thus, the amount of top band is a proxy for the extent of KATP channel surface expression. Note the blots shown for R74X and E128X are from two separate experiments; therefore, signal intensity should be compared within each blot only. (D) Chemiluminescence assays performed to assess surface expression of E128X KATP channels. Surface expression is shown relative to WT channel expression. Error bars represent SEM; n = 3–6 for each condition.