Figure 2.
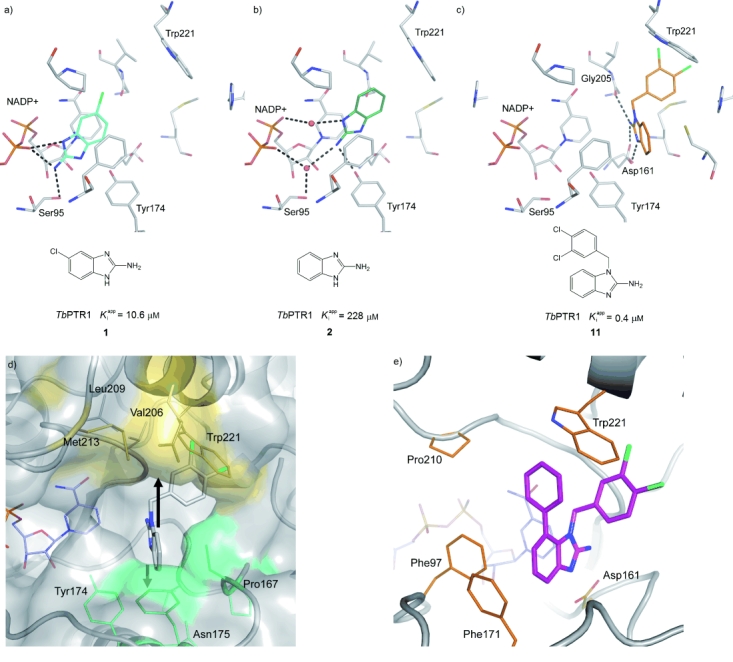
Depending on the substitution pattern, the aminobenzimidazole scaffold adopts three different binding modes. Crystal structures of the inhibitors are shown as follows:13 a) With only a small substitution in the 6-position, the inhibitor forms direct hydrogen bonds with the phosphate group of the co-factor NADP+. b) The unsubstituted scaffold forms water-mediated hydrogen bonds (red spheres) with the phosphate group of NADP+. c) When the scaffold is substituted at N1, the compound binds in an area of the binding site that is perpendicular to the canonical binding site.13 d) Hydrophobic pockets accessible by substitution of compound 11. The surfaces of the pockets for substitutions at the 7- and 4-positions of 11 are coloured yellow and green, respectively. e) X-ray crystal structure of compound 32 (shown in magenta) showing use of the 7’ hydrophobic pocket and the edge–face interaction of the 7-phenyl group with Trp221.
