Table 1.
Activity of N1- and N2-substituted compounds against TbPTR1
| Compd | R1 group | R2 group |
TbPTR1 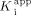 [μm][a] [μm][a]
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 2[b] | H | H | 288 |
| 3[b] | Et | H | >200 |
| 4 | C(=O)Ph | H | >60 |
| 5[b] | CH2CH2Ph | H | 24 |
| 6 | CH2Ph | H | 16 |
| 7 | CH2-(2-chlorobenzene) | H | 10 |
| 8 | CH2-(3-chlorobenzene) | H | 7.5 |
| 9 | CH2-(4-chlorobenzene) | H | 5.4 |
| 10 | CH2-(2,5-dichlorobenzene) | H | 3.7 |
| 11[b] | CH2-(3,4-dichlorobenzene) | H | 0.4 |
| 12 | CH2-(3,5-dichlorobenzene) | H | 8.8 |
| 13 | CH2-(2-methylbenzene) | H | 15 |
| 14 | CH2-(2-fluorobenzene) | H | 21 |
| 15 | CH2-(4-methylbenzene) | H | 15 |
| 16 | CH2-(4-tert-butylbenzene) | H | 4.2 |
| 17 | CH2-(3-trifluoromethylbenzene) | H | 6.3 |
| 18 | CH2-(4-bromobenzene) | H | 3.1 |
| 19 | CH2-pyrid-2-yl | H | 53 |
| 20 | CH2-pyrid-3-yl | H | 54 |
| 21 | CH2-naphth-1-yl | H | 6.1 |
| 22 | CH2-naphth-2-yl | H | 2.8 |
| 23 | CH2-(3,4-dichlorobenzene) | C(=O)CH3 | >60 |
