Figure 1.
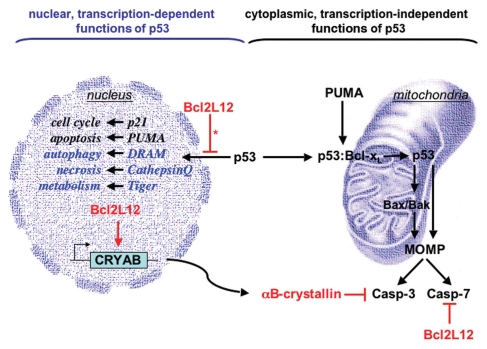
Nuclear and cytoplasmic anti-apoptotic activities of Bcl2L12. Bcl2L12 inhibits p53's transactivational activity and consequently abrogates transcription of selective cell cycle and apoptosis modulators, such as p21 and PUMA (left, nuclear, transcription-dependent functions). Bcl2L12's impact on p53-insigated autophagy, necrosis and metabolism-related pathways (representative targets highlighted in blue) require further studies. In the cytosol (right panel), p53 has direct apoptogenic activities at the level of mitochondria. Here, PUMA can displace p53 from an inhibitory p53:Bcl-xL complex. Released p53 can act as a ‘BH3’-only activator of Bax/Bak to induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and subsequent caspase activation. Besides impacting p53, Bcl2L12 is a well-characterized inhibitor of postmitochondrial effector caspase activation, as it binds to and inhibits caspase-7 (Casp-7) and upregulates the small heat shock protein and caspase-3-specific inhibitor αB-crystallin (CRYAB). *, of note, Bcl2L12 selectively impacts p53 transcription and promoter occupancy.