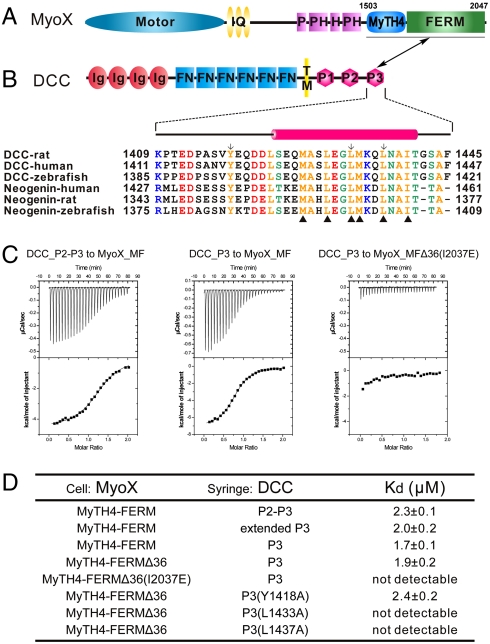
Fig. 1.
Characterization of the MyoX_MF/DCC_P3 interaction. (A and B) The domain organizations of MyoX and DCC. The boundary of MyoX_MF is indicated. The MyoX_MF/DCC_P3 interaction is indicated by a two-way arrow. The sequence alignment of the P3 motif of DCC and neogenin from different species is included. The residues involved in the MyoX_MF/DCC_P3 interaction are indicated by triangle ups. The residues substituted with Ala to test their role in binding to MyoX_MF are labeled by arrows. (C) The ITC curves show the interactions between MyoX_MF and the different DCC cytoplasmic fragments. The MyoX_MF construct with 36-residue deletion in the FERM domain is indicated as MyoX_MFΔ36. (D) The dissociation constants of the binding reactions of various forms of MyoX_MF and DCC obtained from ITC-based assays. The boundaries for the DCC fragments are residues 1321–1445 for P2–P3, 1370–1445 for the extended P3, and 1409–1445 for P3.