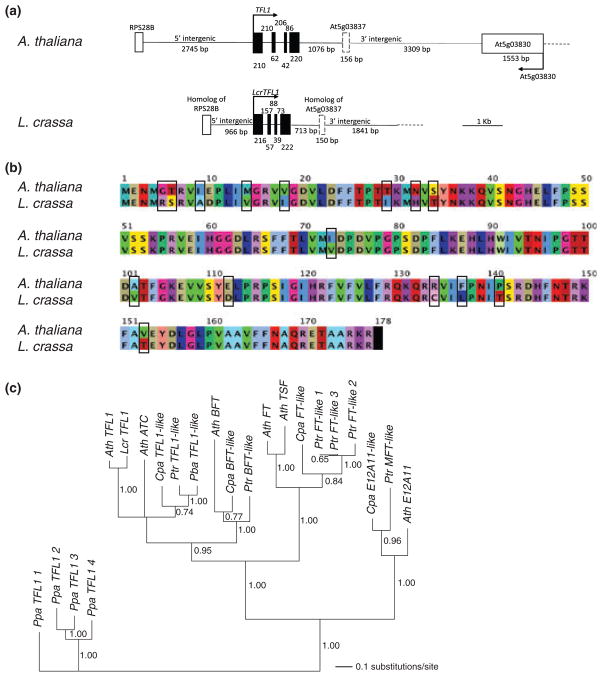
Fig. 2. Leavenworthia crassa TFL1.
(LcrTFL1) is orthologous to the Arabidopsis thaliana gene TFL1. (a) Structure of the LcrTFL1 and TFL1 loci. (b) Alignment of the inferred protein sequences of LcrTFL1 and TFL1. The amino acid differences are boxed. (c) A phylogenetic tree estimate from the coding sequences (CDS) of various members of the TFL1 gene family. This tree is a majority-rule consensus tree based on the post-burn-in tree from two Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo runs of 2 000 000 generations each, applying the generalized time-reversible (GTR) + Γ model of molecular evolution. Values on branches are clade posterior probabilities. Branch lengths (substitutions/site) are the mean branch lengths across trees in the posterior that have the branch. Bayesian analysis of the amino acid sequence from the same genes (using the Whelan and Goldman (WAG) model of protein evolution) yielded a similar tree except that ATC was resolved as sister to Cpa TFL1-like with a 0.99 posterior probability.