Figure. 4.
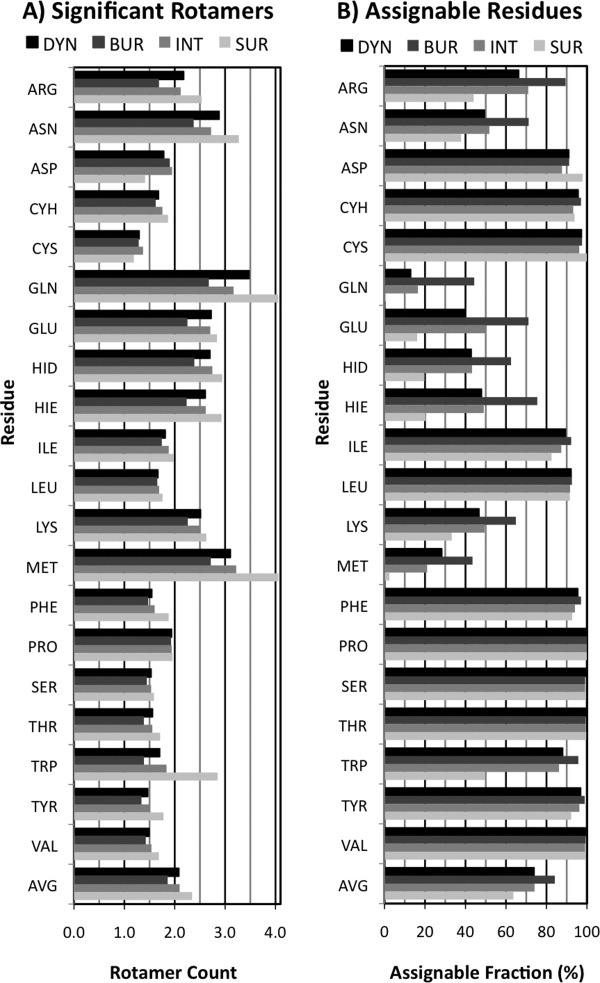
Rotamer Occupancy. A: Significant Rotamers. A typical residue in a protein has two rotamers at > 10% occupancy. Gln and Met occupy the most states while the short amino acids occupy only 1.5 rotamers. Classifying residues by SC-SASA shows residues occupy an extra ½ rotamer when on the surface of a protein compared to when buried. B: Assignable Residues. 75% of residues have a single, unambiguously assignable rotamer conformation (>50% occupancy). Asp, Cyh, Cys, Ile, Leu, Phe, Ser, Thr, Trp, Tyr, and Val are assignable more than 85% of the time. These residues, except for Trp, also show little response to burial. The longer residues, particularly Gln and Met, can be much more difficult to assign the full conformation to.
