Abstract
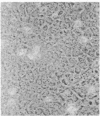
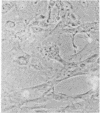
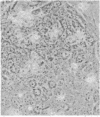
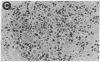
Infection of primary baby rat kidney cells with an adenovirus variant that encodes only the 12S gene of the E1A region, adenovirus type 5 (Ad5) 12S, results in the production of a growth factor that stimulates primary epithelial cells to proliferate. Increased epithelial cell DNA synthesis and proliferation is detectable between 24 and 36 hr after the addition of conditioned medium from Ad5 12S infected cells and not from cells infected with an E1A deletion mutant virus, Ad5 dl312. This mitogenic factor(s) is effective in the absence of serum and can override the inhibitory effect of serum on primary epithelial cells. Furthermore, there is a requirement for the continued presence of the growth factor(s) in the Ad5 12S conditioned medium to maintain epithelial cell proliferation, and the conditioned medium can maintain these cells in a proliferative state for at least 6 wk. The stimulatory activity in Ad5 12S conditioned medium is associated with large molecular weight complexes, from which it can be released by 4 M NaCl. Several characteristics of the growth factor(s) indicate that it is a unique mitogen for epithelial cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D., Sato G. Serum-free cell culture: a unifying approach. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):649–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellett A. J., Li P., David E. T., Mackey E. J., Braithwaite A. W., Cutt J. R. Control functions of adenovirus transformation region E1A gene products in rat and human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1933–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centrella M., Canalis E. Transforming and nontransforming growth factors are present in medium conditioned by fetal rat calvariae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7335–7339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H. Viral DNA in transformed cells. II. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 2 DNA IN NINE LINES OF TRANSFORMED RAT CELLS USING SPECIFIC FRAGMENTS OF THE VIRAL GENOME;. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Hillman D., Berk A. J. Adenovirus early region 1A protein activates transcription of a nonviral gene introduced into mammalian cells by infection or transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1193–1197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon P. B., Conn G., Hatcher V. B. Glycosaminoglycan production in cultures of early and late passage human endothelial cells: the influence of an anionic endothelial cell growth factor and the extracellular matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Dec;125(3):596–607. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Abrahams P. J., Mulder C., Heijneker H. L., Warnaar S. O., De Vries F. A., Fiers W., Van Der Eb A. J. Studies on in vitro transformation by DNA and DNA fragments of human adenoviruses and simian virus 40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):637–650. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation of cloned human beta-globin genes by viral immediate-early gene products. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Growth factors: mechanism of action and relation to oncogenes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. L., Anderson M., Ozanne B. Transforming growth factor(s) production enables cells to grow in the absence of serum: an autocrine system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Pircher R., Krycève-Martinerie C., Jullien P. Normal embryo fibroblasts release transforming growth factors in a latent form. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Oct;121(1):184–188. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Grodzicker T., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Zerler B. Lytic and transforming functions of individual products of the adenovirus E1A gene. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):765–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.765-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Sato G. Fibronectin mediates cytokinesis and growth of rat follicular cells in serum-free medium. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Grodzicker T. Adenovirus E1A 12S protein induces DNA synthesis and proliferation in primary epithelial cells in both the presence and absence of serum. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):673–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.673-682.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Lamb L. C., Newton D. L., Sporn M. B., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Transforming growth factors: isolation of polypeptides from virally and chemically transformed cells by acid/ethanol extraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3494–3498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Eng C. Y., Berk A. J. An adenovirus early region 1A protein is required for maximal viral DNA replication in growth-arrested human cells. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):742–750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.742-750.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel S., Argos P., Philipson L. The release of growth arrest by microinjection of adenovirus E1A DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2329–2336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Ziff E. B. HeLa cell beta-tubulin gene transcription is stimulated by adenovirus 5 in parallel with viral early genes by an E1a-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2792–2801. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles C. D., Capone G. T., Scher C. D., Antoniades H. N., Van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Dual control of cell growth by somatomedins and platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1279–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroobant P., Rice A. P., Gullick W. J., Cheng D. J., Kerr I. M., Waterfield M. D. Purification and characterization of vaccinia virus growth factor. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):383–393. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doren K., Gluzman Y. Efficient transformation of human fibroblasts by adenovirus-simian virus 40 recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1653–1656. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigley C. B., Trejdosiewicz L. K., Southgate J., Coventry R., Ozanne B. Growth factor production during multistage transformation of epithelium in vitro. I. Partial purification and characterisation of the factor(s) from a fully transformed epithelial cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Oct;125(1):156–165. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. C., Jr, Johnstone T. V., Castellot J. J., Karnovsky M. J. Inhibition of rat cervical epithelial cell growth by heparin and its reversal by EGF. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Dec;125(3):499–506. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Moran B., Maruyama K., Moomaw J., Grodzicker T., Ruley H. E. Adenovirus E1A coding sequences that enable ras and pmt oncogenes to transform cultured primary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):887–899. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Growth factors from murine sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4001–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]