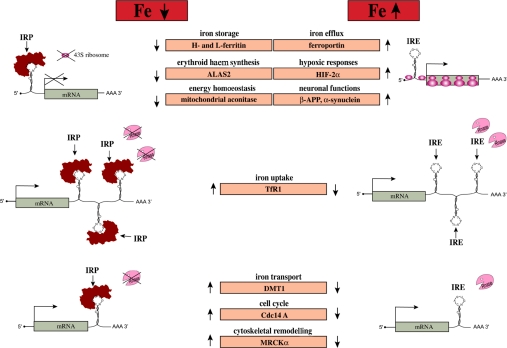
Figure 4. Post-transcriptional control of cellular pathways by the IRE–IRP regulatory system.
Translational-type IRE–IRP interactions in the 5′UTR modulate the expression of the mRNAs encoding H- and L-ferritin, ALAS2, m-aconitase, ferroportin, HIF-2α, β-APP and α-synuclein, which in turn control iron storage, erythroid iron utilization, energy homoeostasis, iron efflux, hypoxic responses and neurological pathways respectively. Conversely, IRE–IRP interactions in the 3′UTR stabilize the mRNAs encoding TfR1, DMT1, Cdc14A and MRCKα, which are involved in iron uptake, iron transport, the cell cycle and cytoskeletal remodelling respectively. Note that the regulation of DMT1, Cdc14A and MRCKα may require additional factors, and that the IREs in Cdc14A and MRCKα mRNAs are not phylogenetically conserved.