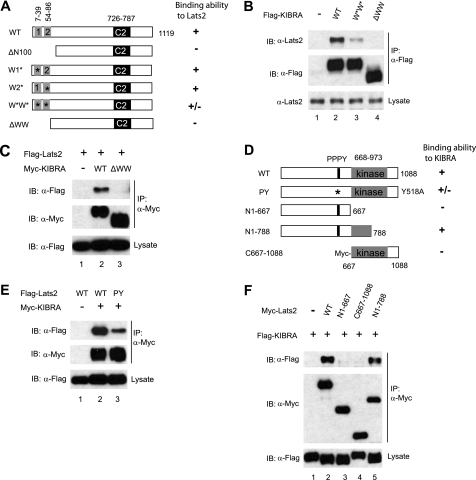
FIGURE 2.
The WW domains of KIBRA are required for its binding to Lats2. A, schematic diagram of various KIBRA constructs. Boxed 1 and 2 represent the first (amino acids 7–39) and the second (amino acids 54–86) WW domain, respectively. C2, C2-like domain; ΔN100, N-terminal 100-amino acid deletion; W1*, the first WW domain mutant (W34A/P37A); W2*, the second WW domain mutant (P84A); W*W*, KIBRA with mutations at both WW domains (W34A/P37A and P84A); ΔWW, amino acids 1–86 deletion. B, FLAG-tagged KIBRA constructs were transfected into HEK293T cells as indicated. At 48 h after transfection, cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody. Immunoprecipitated products were subjected to Western blot with Lats2 antibody to check the presence of endogenous Lats2. C, HEK293T cells were co-transfected with the indicated DNAs. IPs and Western blots were done as in B. D, schematic diagram of Lats2 constructs. Both the PPPY motif and the kinase domains are shown. E, Myc-tagged KIBRA and FLAG-tagged Lats2 (WT and PY mutant) were transfected into HEK293T cells as indicated. At 48 h after transfection, cells were lysed, immunoprecipitated, and subjected to Western blot analysis with indicated antibodies to check the presence of the appropriate proteins. F, FLAG-tagged KIBRA was co-transfected with Myc-tagged Lats2 wild-type or mutant constructs as indicated. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, cells were lysed, and proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc and subjected to Western blotting to probe for FLAG-tagged KIBRA. IB, immunoblot.