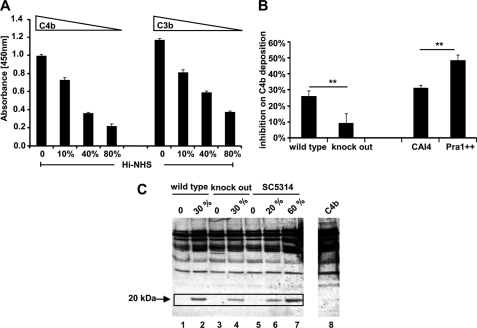
FIGURE 9.
Function of C. albicans-recruited C4BP from normal human serum. A and B, C. albicans-recruited C4BP blocks C4b and C3b surface deposition. C. albicans yeast cells (SC5314) were cultivated overnight in YPD medium at 30 °C, washed by DPBS, and immobilized onto an ELISA plate in RPMI1640 medium overnight at 37 °C (1 × 106/well). Wells were blocked using milk powder (4%), supplemented with BSA (1%) and Tween 20 (0.05%) in DPBS for 2 h at 37 °C. After washing with DPBS, different amounts of Hi-NHS diluted in DPBS were added to the wells. The mixture was incubated for 40 min at 37 °C. After washing, ΔFactor B-HS (7.5%) (Calbiochem) diluted in GVB++ buffer or buffer alone (background control) was added to C. albicans. The mixture was further incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. Following washing with DPBS plus Tween 20 (0.05%), C4b and C3b surface deposition were determined using polyclonal goat anti-C4 (1:5000) or goat anti-C3 (1:5000) serum, followed by horseradish peroxidase conjugated-rabbit anti-goat serum as a secondary antiserum (1:2000). Surface-attached C4BP inhibited C4b and C3b deposition onto the fungal surface in a dose-dependent manner (A). When 30% Hi-NHS was used to incubate with different C. albicans strains, C4b surface deposition was inhibited on wild type RM1000 strain by about 26%. The inhibitory effect on the knock-out strain was about 9% and thus lower. Moreover, C4b surface deposition was more efficiently inhibited on the Pra1-overexpressing strain as compared with the wild type strain (CAI4) (B). Data represent the mean values ± S.D. (error bars) of three separate experiments. C, cofactor activity of C. albicans recruited C4BP from human serum. C. albicans yeast cells (wild type RM1000 and the corresponding Pra1 knock-out mutant and the laboratory reference strain SC5314) (1 × 106/well) were coated onto the ELISA plate in PRMI1640 medium overnight at 37 °C. After blocking with blocking buffer I for 2 h at room temperature, ΔFactor H-HS diluted in DPBS, supplemented with EDTA (10 mm), was added to C. albicans for 1 h at 37 °C. After washing, C4b (5 μg/ml) together with Factor I (0.5 μg/ml) were added. After incubation for 30 min at 37 °C, the supernatant was separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and transferred onto the membrane. The C4b cleavage fragments were detected by Western blotting using polyclonal goat C4 antiserum (1:1000). C4BP bound to C. albicans displays cofactor activity, indicated as the appearance of the 20-kDa cleavage product (boxed, lanes 1 and 2, for the C. albicans wild type strain RM1000, lanes 3 and 4 for the corresponding Pra1 knock-out mutant, and lanes 5–7 for the reference strain SC5314). Lane 8 shows the C4b protein alone. The data show a representative result of three separate experiments.