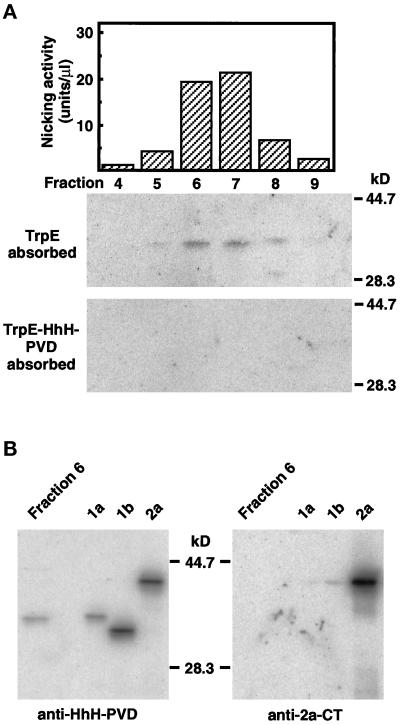
Figure 4.
Chromatographic identification of nuclear OGG1 protein in human cells. (A) RESOURCE S column chromatography of 8-oxoG DNA glycosylase and OGG1 protein present in nuclear extracts prepared from Jurkat cells. The extracts were applied to successive column chromatographies, as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. The flow-through fraction from the RESOURCE Q column that contains activity introducing a nick adjacent to 8-oxoG paired with cytosine in double-stranded oligonucleotides was loaded onto a RESOURCE S column. The active fractions were eluted at 225–350 mM KCl (top). Fractions (70 μl each) eluted from the column were analyzed by Western blotting, using anti–HhH-PVD, which was preincubated with TrpE–Sepharose (middle) or TrpE-HhH-PVD–Sepharose (bottom). (B) Identification of human OGG1–1a in a partially purified preparation of the nuclear 8-oxoG DNA glycosylase. Fraction 6 (70 μl) eluted from RESOURCE S column and recombinant OGG1 proteins expressed in E. coli (OGG1–1a, -1b, and -2a) were subjected to Western blotting, using anti–HhH-PVD and anti–2a-CT.