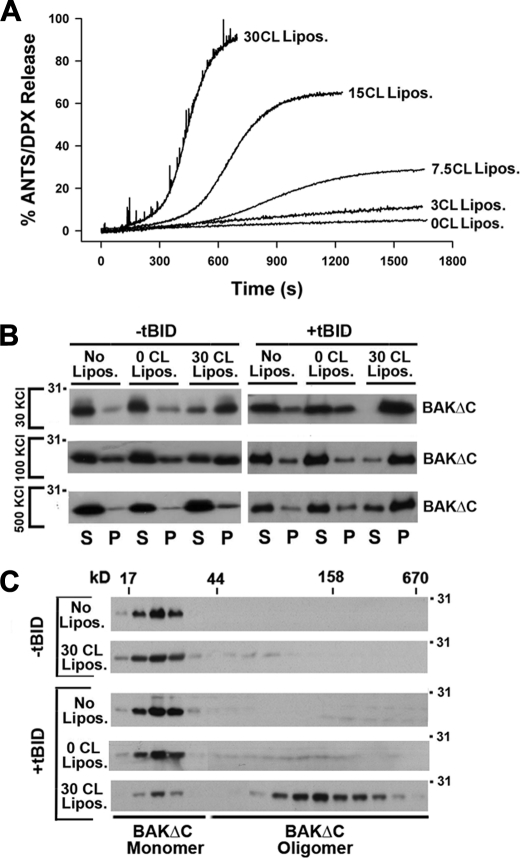
FIGURE 2.
Implication of CL in tBID-triggered functional activation of BAK. A, representative kinetics of ANTS/DPX release induced by BAKΔC (200 nm) plus tBID (100 nm) in LUVs (100 μm) containing lipid mixtures at the indicated the mol/mol ratios: 55PC/35PE/10PI (0CL Lipos.), 52PC/35PE/10PI/3CL (3CL Lipos.), 42.5PC/35 PE/10PI/7.5CL (7.5CL Lipos.), 40PC/35PE/10PI/15CL (15CL Lipos.), and 25PC/35PE/10PI/30CL (30CL Lipos.). B, lipid co-sedimentation assays are shown. BAKΔC (200 nm) with or without tBID (100 nm) was incubated for 20 min with freeze/thaw liposomes composed of 30BrPC/30PC/30PE/10PI (0CL Lipos.) or 30BrPC/30PE/10PI/30CL (30CL Lipos.) followed by sedimentation of the liposomes by low speed centrifugation, and immunoblot analysis of BAKΔC contents in the liposome-containing (P) and liposome-free (S) fractions using anti-BAK G23 polyclonal antibody is shown. Representative gels from at least three independent experiments are shown. No Lipos. corresponds to samples where proteins were incubated without liposomes. C, gel-filtration analysis of BAKΔC on Superdex 200 is shown. The indicated samples were treated with 2% CHAPS (w/v) applied to the column equilibrated with KHE + 2% CHAPS (w/v), and every second elution fraction was analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting using anti-BAK G23 polyclonal antibody. Elution profiles of the molecular weight markers are indicated on the top.