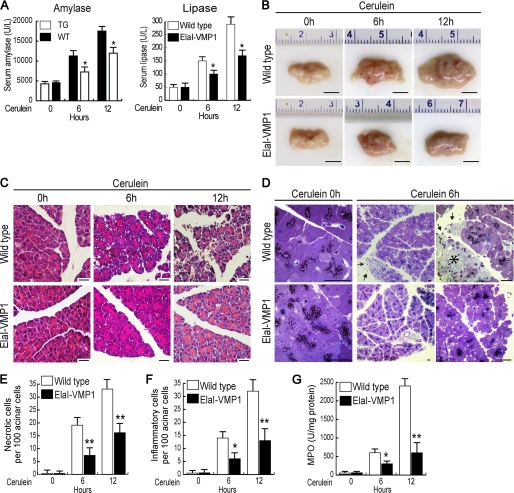
FIGURE 4.
Zymophagy protects acinar cells from trypsinogen (TG) activation mediated by CCK-R hyperstimulation in vivo. Experimental acute pancreatitis was induced in mice by CCK-R hyperstimulation with cerulein. A, amylase and lipase activities in serum from wild type and ElaI-VMP1 mice after cerulein treatment in a time course scheme showing significantly reduced enzyme levels in ElaI-VMP1 mice. B, macroscopic photographs of freshly removed pancreata from wild type and ElaI-VMP1 mice after experimental acute pancreatitis. C, light microscopy of pancreatic tissue from cerulein-treated wild type and ElaI-VMP1 mice using paraffin sections stained with H&E. D, thin plastic section of wild type and ElaI-VMP1 pancreata stained with toluidine blue at increasing magnifications. Images show high degree of necrosis (*) as well as infiltration (arrows) in wild type mice after 6 h of acute pancreatitis. In contrast, almost no inflammation or evidence of necrosis is seen in cerulein-treated ElaI-VMP1 mice. E, necrosis quantification determined in H&E specimens as necrotic cells per 100 acinar cells. F, infiltration quantified in H&E specimens as number of inflammatory cells per 100 pancreatic acinar cells. G, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity determined in pancreas homogenates. Error bars indicate standard deviation of at least three independent experiments (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001 versus wild type). Scale bars, 0.5 cm (B), and 20 μm (C and D).