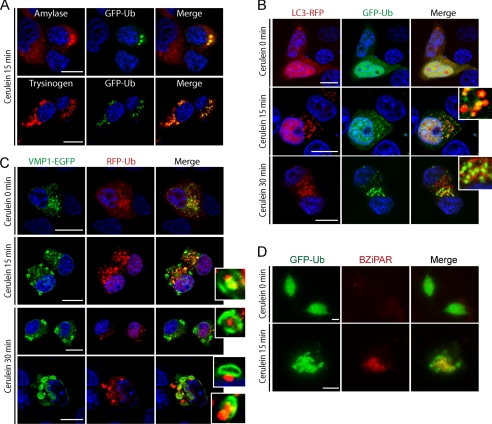
FIGURE 6.
Ubiquitin system serves as a target signal for zymogen granules during zymophagy. Dexamethasone-differentiated AR42J cells were evaluated for ubiquitin participation in the zymophagy process. A, differentiated AR42J cells transfected with GFP-Ub expression plasmid were subjected to cerulein treatment for 30 min, and immunofluorescence assays were made using anti-amylase and anti-trypsinogen antibodies as zymogen granules markers. Large aggregates of ubiquitin and zymogen granules are observed in cell cytoplasm upon CCK-R hyperstimulation. B, acinar cells concomitantly transfected with pRFP-LC3 and GFP-Ub expression plasmids during CCK-R hyperstimulation. Both proteins remain with a diffuse pattern in untreated cells. After 15 min of cerulein treatment there is recruitment of ubiquitin inside LC3 vesicles (detailed), indicating the autophagic engulfment of ubiquitinated granules. C, differentiated AR42J cells cotransfected with pEGFP-VMP1 and pRFP-Ub expression plasmids. Almost no colocalization and diffuse ubiquitin pattern is shown in untreated acinar cells. Under cerulein-mediated CCK-R hyperstimulation, the engulfment of large ubiquitin aggregates by VMP1-vesicles is observed (see details on the right). D, trypsin activity evaluated by BZiPAR specific fluorescent substrate in GFP-Ub transfected acinar cells. Neither trypsin activity nor ubiquitin aggregation is evident in untreated cells. Colocalization between activated zymogen granules and ubiquitin in cerulein-treated cells indicates that ubiquitin system serves as a recognition signal during zymophagy. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bars, 10 μm.