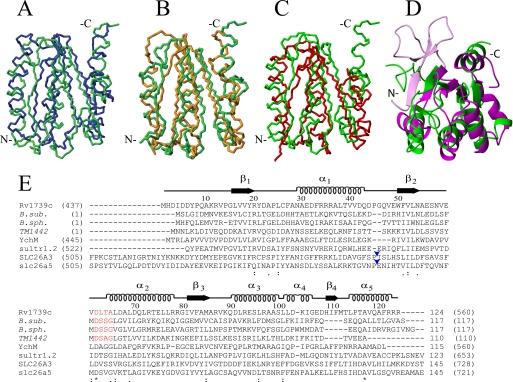
FIGURE 3.
Structural and sequence alignment of Rv1739c STAS domain. A–D, average backbone structure of the Rv1739c STAS domain (green) aligned with: in A, crystal structure of non-phosphorylated SPOIIAA from B. sphaericus (blue, PDB code 1H4Z, root mean square deviation 3.6 Å); in B, solution NMR structure of B. subtilis SPOIIAA (orange, PDB code 1AUZ, root mean square deviation 3.9 Å); in C, solution NMR structure of T. maritima TM1442 (red, PDB 1SBO, root mean square deviation 3.3 Å); in D, overlay of a ribbon representation of Rv1739c STAS (green) with the crystal structure of an engineered core STAS domain from rat Slc26A5/prestin (magenta, PDB code 3LLO, root mean square deviation 3.3 Å). The region shown in light magenta comprises the N-terminal 15 aa of the prestin STAS (light magenta) extending beyond the Rv1739c STAS N-terminal residues. Backbone N, Cα, and C′ atoms were superposed onto secondary structured regions. (Overlays were obtained by superposition of backbone atoms as follows: in A, Rv1739c STAS domain residues 16–20, 30–42, 49–54, 65–77, 81–85, 91–98, and 114–120 were superposed on B. sphaericus SPOIIAA residues 12–16, 23–35, 44–49, 57–69, 76–80, 84–91, and 104–110. In B, STAS domain residues 16–20, 30–42, 49–54, 65–77, 81–85, and 91–97 were superposed on B. subtilis SPOIIAA residues 12–16, 25–37, 44–49, 60–72, 76–80, and 87–93. In C, STAS domain residues 16–20, 30–42, 50–54, 65–77, and 82–86 were superposed on TM1442 residues 14–18, 30–42, 46–50, 59–71, and 78–82. In D, Rv1739c STAS domain residues 16–20, 49–54, 65–77, 81–85, 91–98, and 110–111 were superposed on rat prestin STAS residues 536–540, 640–645, 655–667, 673–677, 681–688, and 702–703.) E, amino acid sequence alignment (ClustalW with manual adjustments) of Rv1739c STAS with STAS domains and structurally characterized anti-σ factor antagonists (italicized) from other organisms, including SpoIIAA from B. subtilis (B. sub.); SpoIIAA from B. sphericus (B. sph.), and TM1442 (T. maritima). Above the aligned sequences are the tertiary structural elements and aa numbers of Rv1739c STAS. Numbers in parentheses are the aa residues encompassing each STAS domain or each (full-length) anti-σ factor antagonist. The conserved DSSG motif of B. subtilis SpoIIAA (red) and its phosphorylated residue Ser58 correspond to DLTA and Thr64 of Rv1739c STAS (red). The STAS domains from E. coli YchM and Sultr1.2 from A. thaliana are of lengths comparable with that of Rv1739c. The STAS domain of 764 aa human SLC26A3/DRA encompasses aa 505–728, and that of rat slc26a5/prestin encompasses aa 505–721. Both are shown with excision of the IVS region of ∼75 aa between helix α1 and strand β2 (blue arrowheads, Rv1739c STAS-based nomenclature (28)). Numbers without parentheses at alignment C termini show lengths of the depicted sequences. In parentheses are the number of aa residues in each full-length polypeptide. Asterisks under the sequences mark positions of complete sequence conservation.