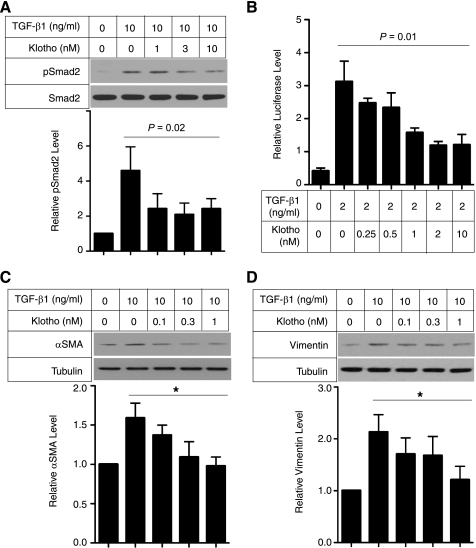
FIGURE 5.
Klotho protein inhibits TGF-β1 signaling and suppresses expression of mesenchymal markers in cultured cells. A, Klotho inhibits TGF-β1-induced phosphorylation of Smad2. NRK52E renal epithelial cells were incubated with secreted Klotho protein at the indicated doses for 30 min and then stimulated with TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) for 30 min. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibody against phosphorylated Smad2 (pSmad2) or antibody that recognized Smad2 regardless of its phosphorylation state (Smad2). Typical results of 5 independent experiments are shown (upper panel). pSmad2/Smad2 ratios in each treatment were normalized with those without TGF-β1 and Klotho. Data indicate means ± S.E. of five independent experiments (lower panel). p = 0.02 by one-way ANOVA. B, Klotho inhibits TGF-β1-induced activation of a Smad-responsive reporter. HEK293 cells were transfected with a luciferase reporter containing Smad response elements (pGTCT2 × 2-Luc) and a lacZ expression vector for normalization. These cells were incubated with TGF-β1 and/or Klotho at the indicated doses and subjected to standard luciferase assays. Data indicate means ± S.E. of three independent experiments. p = 0.01 by one-way ANOVA. C, Klotho suppresses TGF-β1-induced increase in α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA) protein. NRK52E cells were incubated with Klotho protein and TGF-β1 at the indicated doses for 48 h in DMEM supplemented with 1% FBS. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies against αSMA and tubulin. A typical result of five independent experiments was shown (upper panel). The αSMA/tubulin ratios in each treatment were normalized with those without treatment. Data indicate means ± S.E. of five independent experiments (lower panel). *, p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA. D, same as C, except that anti-Vimentin antibody was used.