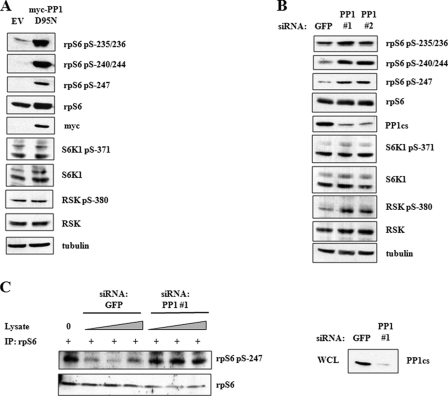
FIGURE 4.
PP1 regulates rpS6 dephosphorylation. A, dominant-negative PP1 induces rpS6 phosphorylation. HEK 293T cells were transfected with empty vector (EV) or plasmids encoding Myc-tagged PP1D95N for 24 h. Cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using α-P-rpS6-235/236, α-P-rpS6-240/244, α-P-rpS6-247, α-rpS6, α-Myc, α-P-S6K1-371, α-S6K1, α-P-RSK-380, α-RSK, and α-tubulin antibodies. B, siRNA knockdown of PP1 induces rpS6 phosphorylation. HEK 293T cells were transfected with siRNA directed against GFP or PP1cs for 48 h. Cells were serum-starved 24 h prior to harvesting. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with α-P-rpS6-235/236, α-P-rpS6-240/244, α-P-rpS6-247, α-rpS6, α-PP1, α-P-S6K1-371, α-S6K1, α-P-RSK-380, α-RSK, and α-tubulin antibodies. C, PP1 dephosphorylates rpS6 in vitro. HEK 293T extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with α-P-rpS6-235/236 antibody. Immunoprecipitates (IP) were mixed for 30 min at 37 °C with HEK 293T whole cell lysates that were transfected with siRNA directed against either GFP or PP1. Precipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with α-P-rpS6-247 and α-rpS6 antibodies. Whole cell lysates (WCL) from siRNA-transfected cells were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with α-PP1 antibody. These data are representative of three independent experiments.