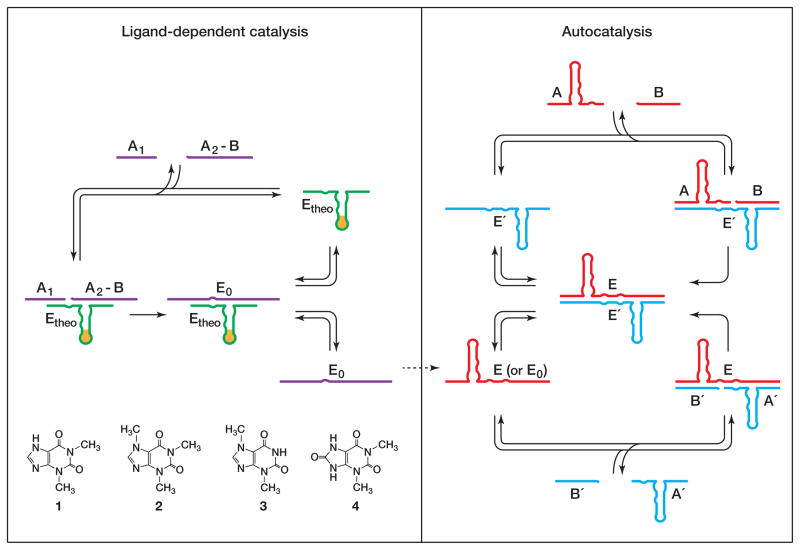
Figure 1.
Scheme for ligand-dependent exponential amplification, coupling ligand-dependent catalysis (left) to ligand-independent autocatalysis (right). The ligand is recognized by an aptamer domain that is linked to an RNA ligase enzyme (Etheo). In the presence of the cognate ligand 1, but not closely-related compounds 2–4, Etheo catalyzes the joining of two oligonucleotide substrates (A1 and A2-B) to form ligase enzymes (E0) that can seed exponential amplification. Exponential amplification involves two ligase enzymes (E and E′) that catalyze each other’s synthesis from a total of four component substrates (A and B, and A′ and B′, respectively).