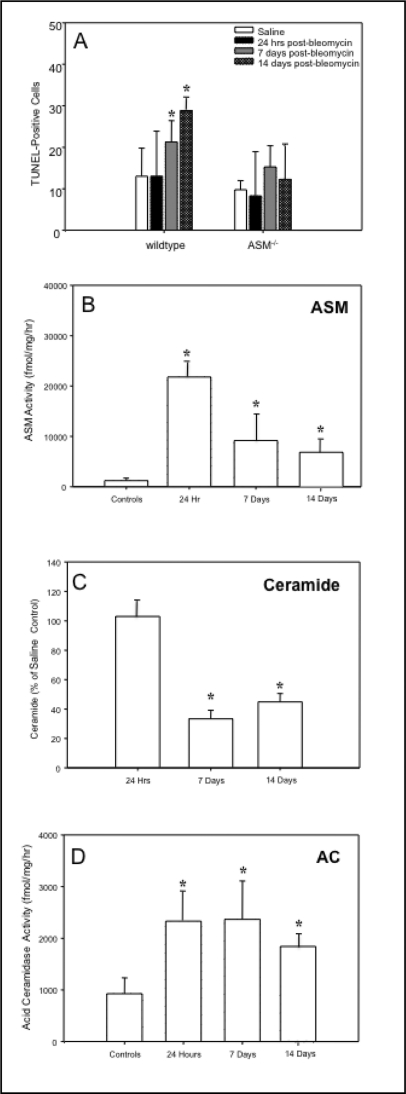
Fig. 4.
The sphingomyelin/ceramide apoptosis pathway in bleomycin-instilled lungs. The numbers of TUNEL positive lung cells were significantly increased in wildtype mice starting at 7 days post-bleomycin treatment, whereas there was no significant change in the numbers of apoptotic cells in ASM−/− mouse lungs (A). Sections from 6 animals/group were analyzed. Representative images are shown. ASM activity also was significantly elevated in wildtype mice 24 hrs after bleomycin instillation and while reduced by 7 and 14 days, remained significantly higher than control (saline injected) mice (B). The ceramide levels in the lungs of bleomycin-treated wildtype mice were equivalent to the saline-injected controls at 24 hr, and at 7 and 14 days were significantly reduced compared with saline- treated controls (C). The acid ceramidase (AC) activity in wildtype lungs was increased at 24 hr and remained significantly elevated for up to 14 days (D). * indicates significant differences from control (saline-injected) and bleomycin-treated animals (p value <0.05).