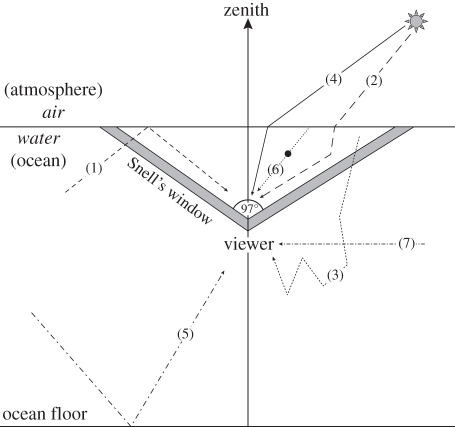
Figure 1.
Processes affecting underwater polarization of celestial illumination: (1) internal reflection from the sea surface, (2) single scattering, (3) multiple scattering, (4) refraction of direct light while travelling from air to water, (5) reflection from the sea floor, (6) forward scattering and (7) attenuation of polarized light. The thick grey lines delineate the boundaries of Snell's window with an acceptance angle of 97°. After Sabbah et al. [2].