Figure 8.
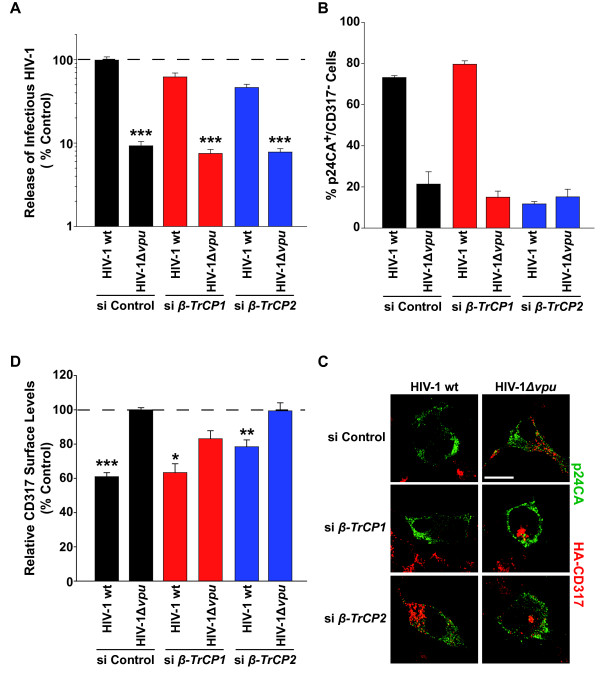
Vpu antagonism coincides with a reduction of CD317 surface levels, not depletion of intracellular pools of the restriction factor in HIV-infected cells. 293HA-CD317 cells were transfected twice with siRNAs targeting either β-TrCP1 or β-TrCP2 or with a control siRNA. Following the second transfection, cells were infected with VSV-G pseudotyped HIV-1 wt or HIV-1Δvpu overnight and washed the following day. Two days post-infection, (A) the yield of infectious HIV-1 in culture supernatants was quantified. The arithmetic means ± SEM of four experiments are shown. (B, C) Half of the infected cultures were processed for microscopic analysis to (C) visualize and (B) quantify the percentage of p24CA-positive (green) cells that no longer express HA-CD317 (red). Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) Shown are arithmetic means of results from two independent experiments. (C) White arrows indicate HA-CD317 expression (red staining) in infected, p24CA-positive (green staining) cells. (D) The other half of the cells was analyzed for surface levels of CD317 on productively infected, p24CA-positive cells by flow cytometry. MFI values for control siRNA-treated cells, infected with Vpu-defective HIV-1, were set to 100%. Remaining cellular mRNA levels for β-TrCP1 and β-TrCP2 were 23 ± 9% and 3 ± 1%, respectively, relative to the control siRNA-treated cells. The arithmetic means ± SEM (n = 9) from three independent experiments are shown. Student's t-test (comparing results for HIV-1 wt and HIV-1Δvpu for each knockdown condition): * p < 0.02, ** p < 0.004, *** p < 10-5. In addition, a statistical significance test was performed for results for HIV-1 wt in si Control-treated versus si β-TrCP2-treated cells in panel A (p < 0.0001) and panel D (p < 0.0017).
