Figure 12.
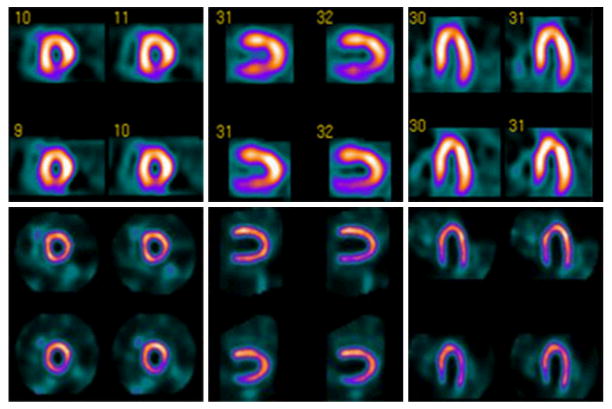
99mTc-sestamibi myocardial perfusion images obtained with conventional SPECT (top) and with novel high-efficiency “D-SPECT” system (bottom) using 99mTc-sestamibi stress/rest gated protocol. High-dose (first row) and low-dose (second row) images acquired with 28 mCi and 10 mCi respectively of 99mTc-sestamibi, and required 16 min and 20 min with conventional SPECT versus 4 min and 2 min with D-SPECT. Conventional SPECT interpreted as having reversible inferior wall defect. D-SPECT interpreted as normal and was confirmed by coronary angiography. (Courtesy of Spectrum Dynamics, Ltd.)
