Table 1.
Modification of Region II (Linker)
| Compd | Analogue | na | IC50b (μM) | Kdc (μM) | Activation of Viral Infectivityd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 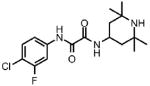 |
67 | 74.8 ± 5.4 | 0.76 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 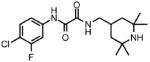 |
1 | 33.0 | 2.2 | 0.09 |
| 3 | 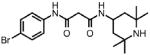 |
1 | >100.0 | N.D. | 0.0 |
| 4 | 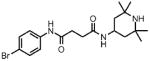 |
1 | >100.0 | N.D. | 0.0 |
| 5 | 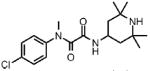 |
1 | >100.0 | N.D. | 0.0 |
| 6 | 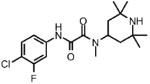 |
1 | >100.0 | N.D. | 0.0 |
| 7 | 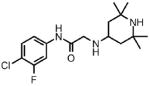 |
1 | >100.0 | N.D. | 0.0 |
Each compound was assayed in triplicate and is reported as a mean for one experiment. For multiple experiments the means and standard deviations are reported. The number of times independent experiments were performed is indicated by n.
The compound concentrations that inhibited 50% of virus infection (IC50) was determined by infecting Cf2Th-CD4/CCR5 cells with 10,000 RT units of wild-type HIV-1YU2 virus expressing luciferase with increasing concentrations of the compound. Compounds labeled non-specific in the Supplementary Tables where found to have comparable IC50’s when assayed against viruses with the ampotrophic murine leukemia virus (A-MLV) envelop glycoproteins.
Kd’s were measured by isothermal titration calorimetry once, unless otherwise indicated in parentheses.
Activation of viral infectivity was determined by infecting Cf2Th-CCR5 cells with recombinant HIV-1YU2 in the presence of NBD analogs. The luciferase activity in the target cells incubated with each compound was divided by that in the cells incubated with JRC-II-191 to obtain the relative activation of infectivity. ND indicates not determined. NB indicates no detectable binding.
