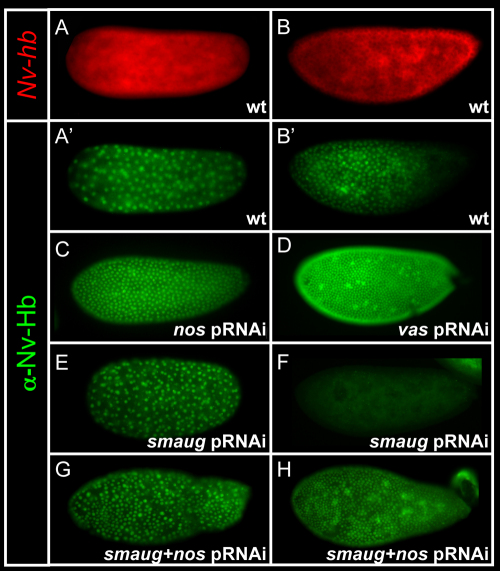
Fig. 3.
Function and regulation of Nv-nos in the early blastoderm. (A,B) Red, Nv-hb mRNA; (A′,B′,C-F) green, Nv-Hb protein. (C-F) Nv-hb mRNA is expressed ubiquitously in all embryos shown, but is omitted for clarity. (A,A′) Early blastoderm wild-type embryo showing ubiquitous expression of Nv-hb mRNA (A) and Hb protein (A′). (B,B′) Later, Nv-hb mRNA (B) is still ubiquitous, while Nv-Hb protein (B′) is repressed from the posterior. (C) After Nv-nos pRNAi, posterior repression of Nv-Hb is lost. (D) Nv-vasa RNAi also results in ectopic Nv-Hb protein in the posterior of the embryo. (E) Expression of Nv-Hb protein in the early embryonic stages is not affected by Nv-smaug RNAi. (F) Loss of Nv-smaug results in repression of Nv-hb throughout the early blastodermal embryo. (G,H) Simultaneous Nv-smaug and nos pRNAi embryo.