Figure 6.
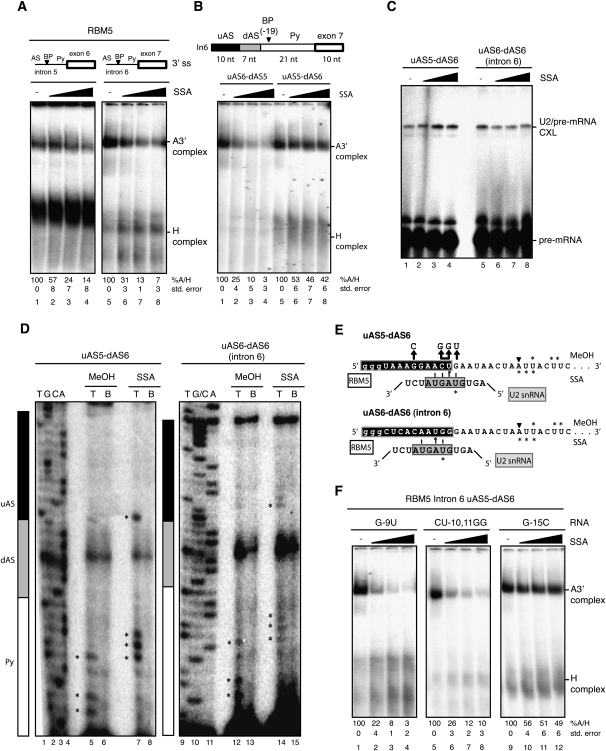
Differential sensitivity to SSA is modulated by sequences upstream of the branch point. (A) Spliceosome assembly assays were carried out as in Figure 1C using RNAs corresponding to RBM5 introns 5 and 6 3′ splice site regions, including the polypyrimidine tract (Py), branch point (BP), and AS. (B) Spliceosome assembly assays (as in A) using chimeric RBM5 intron 6 RNAs in which the indicated sequences have been replaced by the corresponding fragments of intron 5. The length of the different regions of the RNAs used is indicated. (C) Psoralen cross-linking assays (as in Fig. 2B) using the indicated RNAs. (D) Mapping of U2 snRNA/RBM5 intron 6 psoralen-induced cross-links by primer extension in the absence or presence of SSA, as in Figure 2C. Lanes 1–4 and 9–11 correspond to dideoxy sequencing reactions of the corresponding DNA products using the same primer. Asterisks indicate primer extension stops. Black, gray, and white boxes designate the different segments of the 3′ splice site region, as in B. (E) Schematic representation of potential U2 snRNA/RBM5 pre-mRNA base-pairing interactions induced by SSA. Asterisks mark the cross-linked nucleotides mapped in C in methanol- and SSA-treated samples. Nucleotides in the gray box represent the U2 snRNA bprs. (F) Spliceosome assembly assays (as in A) using RNAs harboring mutations (also indicated in E) in the residues proposed to base-pair with U2 snRNA bprs (or control residues) of the uAS5–dAS6 chimeric RNA.