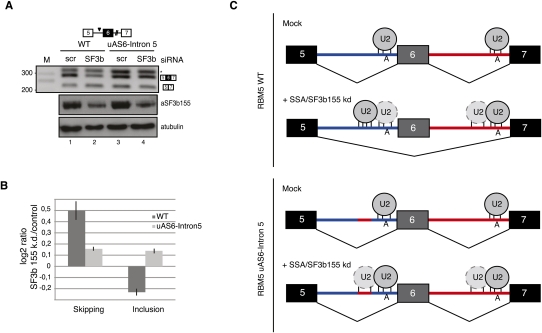
Figure 7.
Base-pairing potential with U2 snRNA of sequences 5′ of the branch point can modulate SSA-induced alternative splicing. (A) RT–PCR analysis of RBM5 RNA isoforms expressed from plasmids expressing the alternatively spliced RBM5 region (exons 5–7), either wild type or a mutant, that replaces the upstream region of the intron 5 AS with the corresponding sequence from intron 6 (uAS6–intron 5) in control cells or in cells in which expression of SF3b 155 has been knocked down. The asterisk indicates an aberrant amplification product caused by primer hybridization in intron 5, as determined by sequencing. The bottom panel shows Western blot analysis of the levels of SF3b 155 and α-tubulin in control and SF3b 155 knockdown cells. (B) Analysis of RBM5 exon 6 skipping and inclusion of RNAs analyzed in A in SF3b 155 knockdown versus control cells by quantitative RT–PCR, using splice junction primers specific for exon inclusion or skipping as one of the oligonucleotides used in the PCR amplification reactions. (C) Mechanistic model for alternative splicing regulation induced by SSA or SF3b155 knockdown. Under normal conditions, both of the branch point regions of RBM5 introns 5 and 6 are occupied by U2 snRNP, and the alternatively spliced exon 6 is preferentially included in mature transcripts. SSA or SF3b knockdown inactivates a fidelity mechanism that prevents U2 snRNP binding to decoy branch point-like sequences 5′ of the functional sites. The presence of a decoy site with strong base-pairing complementarity with U2 snRNA leads to preferential recruitment of the snRNP to this site, inhibition of the intron 5 3′ splice site, and exon skipping. Consistent with this hypothesis, replacement of the decoy sequence by a sequence in intron 6 (uAS6–intron 5) with lower base-pairing potential with U2 snRNA attenuates the effects of SSA/SF3b 155 knockdown. Exons, introns, and branch point adenosines are indicated. The relative base-pairing potential of U2 snRNA with different pre-mRNA sequences is represented by the number of vertical lines.