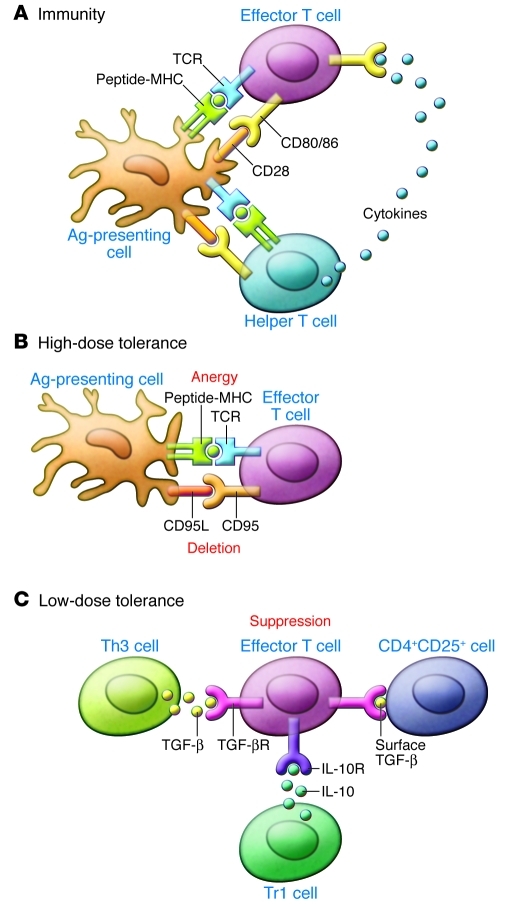
Figure 1. Mechanisms of oral tolerance.
(A) Generation of an immune response requires ligation of the T cell receptor with peptide-MHC complexes in the presence of appropriate costimulatory molecules (CD80 and CD86) and cytokines. (B) With high doses of oral antigen, T cell receptor cross-linking can occur in the absence of costimulation or in the presence of inhibitory ligands (CD95 and CD95 ligand), leading to anergy or deletion, respectively. (C) Low doses of oral antigen lead to the activation of regulatory T cells, which suppress immune responses through soluble or cell surface–associated suppressive cytokines (IL-10 and TGF-β). Adapted from ref. 7 with permission from Elsevier.