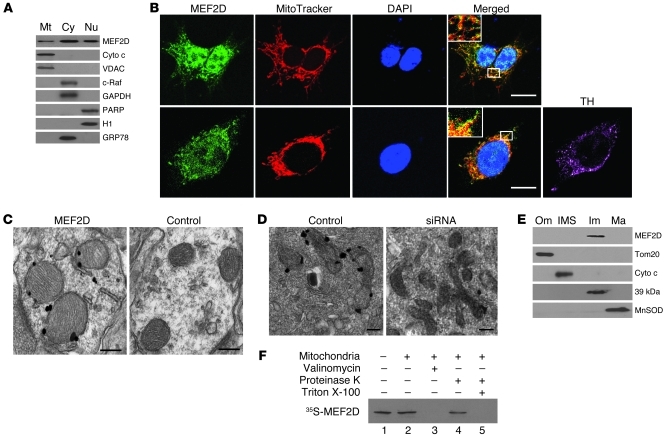
Figure 1. Localization of MEF2D in mitochondria of neuronal cells.
(A) Localization of MEF2D in mitochondria of SN4741 cells (n = 3). Cyto c and VDAC are mitochondrial (Mt) markers; c-Raf and GAPDH are cytoplasmic (Cy) markers; PARP and histone H1 are nuclear (Nu) markers; GRP78 is a ER marker. (B) Colocalization of MEF2D with MitoTracker in both SN4741 cells and primary rat midbrain DA neurons (n = 4). TH is a DA neuron marker. Scale bars: 10 μm. Inset original magnification, ×1,000. (C) Localization of MEF2D in rat brain mitochondria under TEM. The control is without primary antibody (n = 4). Scale bars: 100 nm. (D) Localization of MEF2D in mitochondria of SN4741 cells under TEM (n = 4). Scale bars: 50 nm. (E) Localization of MEF2D in the inner membrane of rat brain mitochondria. Tom20, Cyto c, complex I 39-kDa protein, and MnSOD are markers for mitochondrial outer membrane (Om), inter-membrane space (IMS), inner membrane (Im), and matrix (Ma), respectively. n = 3. (F) In vitro mitochondrial import of MEF2D. Lane 1, MEF2D control (1:10 input); lane 2, imported MEF2D; lane 3, valinomycin-induced (20 μM) loss of membrane potential on MEF2D import; lane 4, resistance to proteinase K digestion after MEF2D import; lane 5, complete digestion of MEF2D by proteinase K after solubilization of mitochondria with Triton X-100. n = 3.