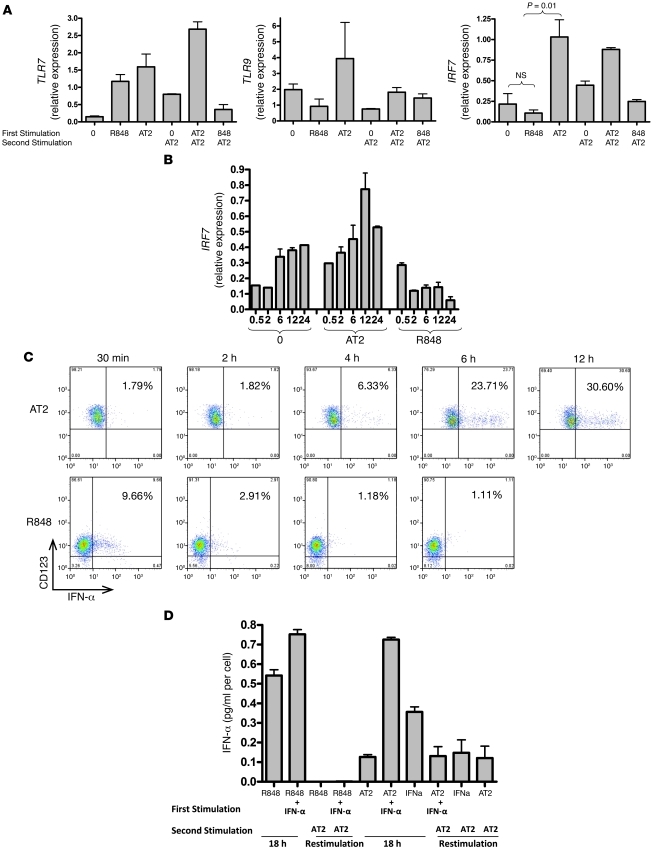
Figure 4. HIV-activated pDCs increase mRNA expression of IRF7, which correlates with ability to produce secondary IFN-α responses.
(A) pDCs were incubated with media alone, AT-2 HIV, or R848 for 18 hours, then washed for immediate preparation of mRNA or washed and placed back in culture with AT-2 HIV for 18 hours. cDNA was prepared for qRT-PCR. Relative expression of gene products was normalized to GAPDH. Whereas TLR7 expression increased in pDCs exposed to either AT-2 HIV or R848, and TLR9 expression was variable, IRF7 expression increased relative to unstimulated pDCs (*P < 0.05; Student’s t test) in AT-2 HIV–exposed pDCs, but decreased in R848-exposed pDCs. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 replicates) and representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) IRF7 expression was spontaneously increased by unstimulated cells and further augmented by AT-2 HIV stimulation, but was decreased by R848 over the time course. (C) R848-stimulated pDCs produced IFN-α within 30 minutes, but were no longer producing by 2–4 hours. In contrast, AT-2 HIV–stimulated pDCs did not begin to produce IFN-α for 6 hours, but continued to produce at 12 hours. Data are representative of 5 independent experiments. (D) To test whether exogenous IFN-α could rescue the block to restimulation with R848, purified pDCs were incubated with IFN-α and R848; again, pDCs could not be restimulated to produce IFN-α (*P < 0.05 versus first stimulation with R848; Student’s t test). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 replicates) and representative of 2 independent experiments.