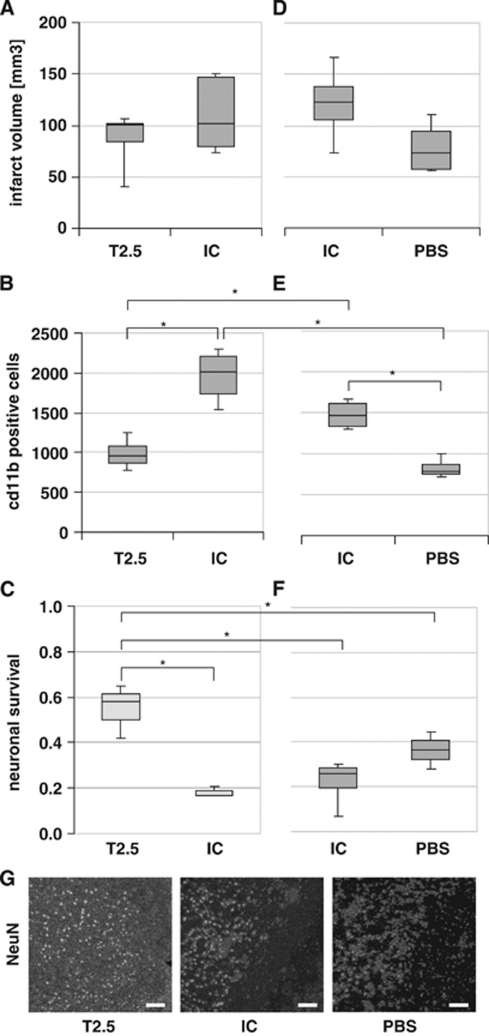
Figure 3.
(A–C) TLR2 inhibition reduces inflammatory response and increases neuronal survival. (A) TLR2 inhibition and its effect on the infarct volume. Direct infarct volume in male C57Bl/6 wild-type mice at 48 hours of reperfusion after 45 minutes middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) treated with 0.05 μg T2.5 anti-TLR2 antibody (T2.5) and 0.05 μg isotype control (IC) antibody, respectively. Values are visualized as box-and-whisker plots (nT2.5=6; nIC=8; P>0.05). (B) TLR2 inhibition and its effect on the inflammatory response. CD11b-positive cells in the postischemic hemisphere at interaural position 3.9 mm at 48 hours after induction of MCAO for 45 minutes in male C57Bl/6 wild-type mice (P<0.001; nT2.5=6; nIC=8). (C) TLR2 inhibition and its effect on neuronal survival. NeuN-positive cells in the postischemic hemisphere at interaural position 3.9 at 48 hours after induction of MCAO for 45 minutes (P<0.05; nT2.5=3; nIC=3). ‘Neuronal survival' is shown, a ratio that was calculated as the number of NeuN-positive cells in the ischemic hemisphere divided by the number of NeuN-positive cells in the nonischemic (contralateral) hemisphere. (D–F) Effect of isotype control antibody on the postischemic brain injury. (D) Application of isotype antibody and its effect on the direct infarct volume. Direct infarct volumes in male C57Bl/6 wild-type mice are shown at 48 hours reperfusion after 45 minutes MCAO treated intraarterially with 0.05 μg isotype control antibody (IC), and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), respectively. Cell counts are visualized as box-and-whisker plots (P>0.05, nIC=4; nPBS=4). (E) Antibody application and its effect on the inflammatory response. CD11b-positive cells in the postischemic hemisphere at interaural position 3.9 mm at 48 hours after induction of MCAO for 45 minutes in male C57Bl/6 wild-type mice (P<0.05, nIC=4; nPBS=4). (F) Antibody application and its effect on neuronal survival. ‘Neuronal survival' ratio was calculated as the number of NeuN-positive cells in the ischemic hemisphere divided by the number of NeuN-positive cells in the nonischemic (contralateral) hemisphere (P>0.05, nIC=4; nPBS=4). Statistical analysis between the different treatment groups of the two separate experiments (T2.5 versus IC, and IC versus PBS) was performed using analysis of variance (P<0.005), followed by pairwise comparisons using the Mann–Whitney U-test. (G) Representative images of NeuN-specific cell stain, located at the infarct border zone in the ischemic hemisphere at interaural position 3.9 at 48 hours of reperfusion after induction of MCAO for 45 minutes in male C57Bl/6 wild-type mice after intraarterial injection of T2.5 anti-TLR2 antibody (T2.5), isotype control (IC) antibody, or PBS, respectively. Scale bar=100 μm. *P<0.05.