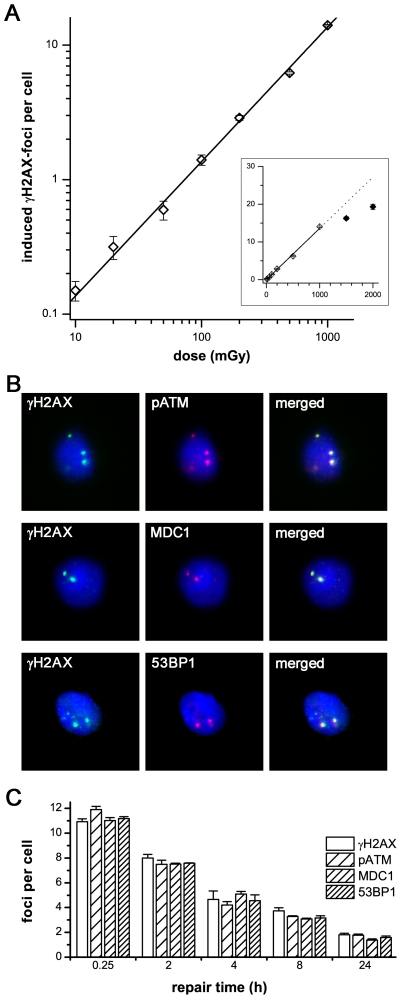
Figure 1. γH2AX-foci in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
A: γH2AX-foci in CD34+ cells were enumerated at 0.5 h after irradiation with doses from 10 mGy to 2000 mGy and plotted against the irradiation dose. The induction of γH2AX-foci is clearly dependent on the irradiation dose, with a linear correlation from 10 mGy to 1000 mGy. At foci levels of more than 15 foci per cell, the clustering of foci impedes their clear discrimination, leading to an underestimation of actual foci numbers (inset). B: Immunofluorescence double-staining of γH2AX (green) combined with pATM, MDC1 or 53BP1 in CD34+ cells, 8 h after irradiation with 2 Gy. The clear co-localization with other DNA repair factors confirms that γH2AX-foci can be used to analyze DSBs. (Original magnification, ×600) C: Quantitative analysis of γH2AX-, pATM-, MDC1- and 53BP1-foci in CD34+ cells at different time-points after irradiation with 1 Gy. γH2AX-foci co-localize consistently with other DNA repair factors. Error bars signify the SE of three different experiments.