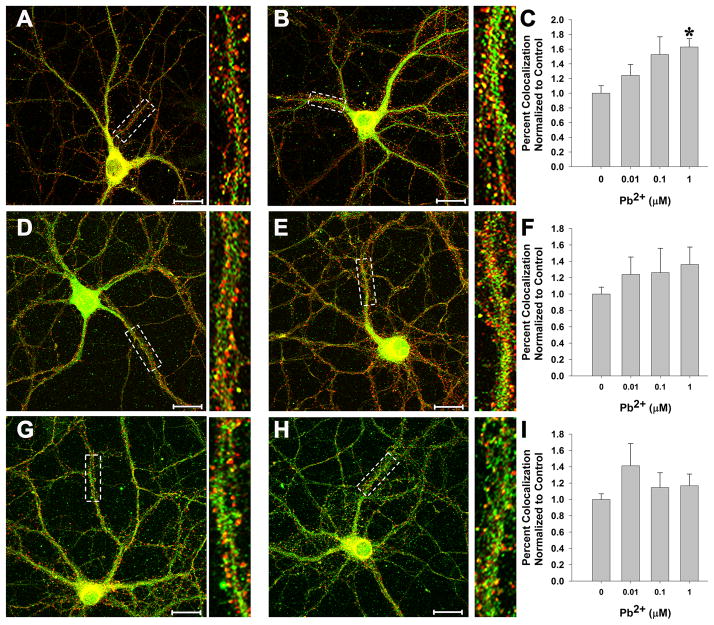
Figure 4. Pb2+ exposure increases NR1 targeting to the PSD.
(A-C) Representative images of control (A) and 1 μM Pb2+ (B)-treated neurons stained for NR1 (green) and PSD95 (red). Colocalization is shown as yellow or orange color. Quantification of colocalization is shown in (C). A significant, concentration-dependent increase in NR1 colocalization with PSD95 was observed after Pb2+ exposure.
(D-F) Representative images of control (D) and 1 μM Pb2+ (E)-treated neurons stained for NR2A (green) and PSD95 (red). Colocalization is shown as yellow or orange color. Quantification of colocalization is shown in (F). No effect on NR2A colocalization with PSD95 was observed after Pb2+ exposure.
(G-I) Representative images of control (G) and 1 μM Pb2+ (H)-treated neurons stained for NR2B (green) and PSD95 (red). Colocalization is shown as yellow or orange color. Quantification of colocalization is shown in (I). No effect on NR2B colocalization with PSD95 was observed after Pb2+ exposure.
Data are shown as the mean ± SEM and are the result of 4 independent trials with 22–26 neurons per condition. * = significance from control (Fisher’s Protected LSD).