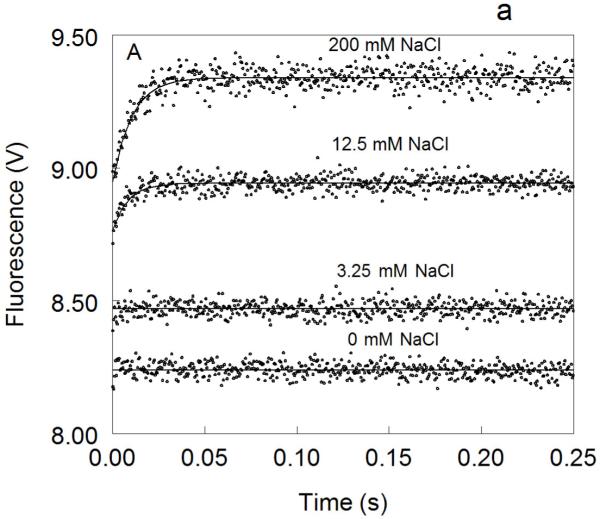
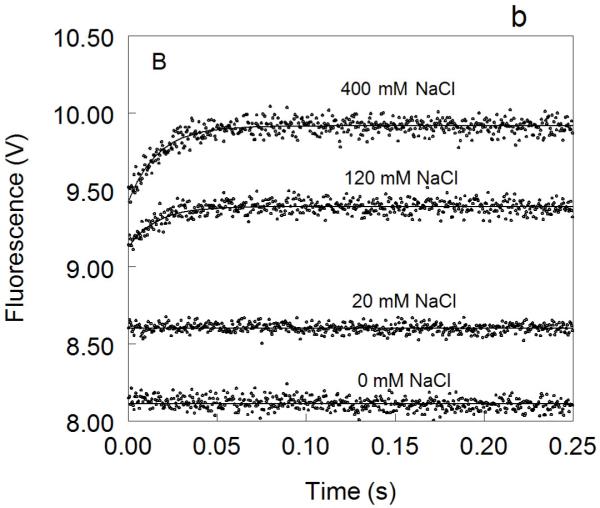
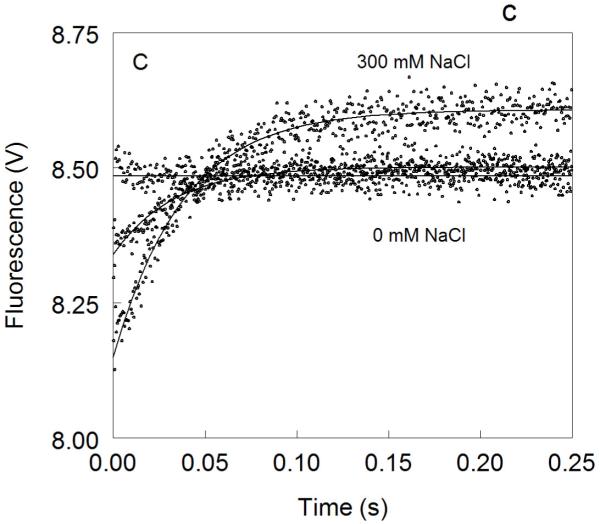
Figure 1. Kinetic traces of Na+ binding to thrombin (A), factor Xa (B) and activated protein C (C).
In all cases binding of Na+ obeys a two-step mechanism, with a fast phase completed within the dead time (<0.5 ms) of the spectrometer, followed by a single-exponential slow phase. The kobs for the slow phase decreases with increasing [Na+] (see also Fig. 2). Experimental conditions are: 100 nM enzyme, 50 mM Tris, 0.1% PEG8000, pH 8.0, at 15 °C. Continuous lines were drawn using the expression b-aexp(−kobst) with best-fit parameters: (A) a=0.000±0.000 V, b=8.239±0.001 V (0 mM Na+); a=0.000±0.000 V, b=8.470±0.001 V (3.25 mM Na+); a=0.175±0.002 V, kobs =120±4 s−1 , b=8.942±0.001 V (12.5 mM Na+); a=0.392±0.001 V, kobs=96±1 s−1 , b=9.340±0.002 V (200 mM Na+). (B) a=0.000±0.000 V, b=8.112±0.001 V (0 mM Na+); a=0.000±0.000 V, b=8.601±0.001 V (20 mM Na+); a=0.261±0.002 V, kobs=64±4 s−1 , b=9.391±0.001 V (120 mM Na+); a=0.488±0.001 V, kobs=60±1 s−1 , b=9.915±0.002 V (400 mM Na+). (C) a=0.000±0.000 V, b=8.485±0.001 V (0 mM Na+); a=0.162±0.001 V, kobs=31±1 s−1 , b=8.501±0.001 V (curve in the middle not labeled, 25 mM Na+); a=0.458±0.001 V, kobs =27±1 s−1 , b=8,608±0.001 V (300 mM Na+). The concentration of Na+ was changed in all cases by adding NaCl without keeping the ionic strength constant. The amplitude of the slow phase for factor Xa and activated protein C becomes less pronounced in the presence of Ca2+ (data not shown), reflecting the positive linkage between Na+ and Ca2+ binding in these proteases 51,52,54-58. Binding of Ca2+ likely shifts the E*-E equilibrium in favor of E. In the case of thrombin, Ca2+ has no effect on Na+ binding.