Abstract
In the title complex, [Mo(C7H5OS)Cl(C18H15P)2(CO)2], the geometry around the metal atom is a capped octahedron. The phenoxythiocarbonyl ligand coordinates the MoII atom through the C and S atoms. A one-dimensional structure is formed by π–π intermolecular interactions and a supramolecular aggregation is determined by intermolecular C—H⋯O, C—H⋯Cl, C—H⋯π(arene) hydrogen bonds and CO⋯π(arene) interactions [O⋯centroid distances = 3.485 (4) and 3.722 (3) Å].
Related literature
For the use of metallocarboxylic acids as intermediates in the homogeneous catalysis of the water gas shift reaction, see: Yoshida et al. (1978 ▶). For O-Aryl thiocarbonate, benzoxazoline-2-thione, chromene-2-thione and N,N-dimethylthiocarbamate metal complexes, see: Chen et al. (1978 ▶); McFarlane et al. (1998 ▶); Zheng et al. (2006 ▶) and Zhang & Shi (2004 ▶), respectively. For phenoxylcarbonyl metal complexes, see: Anderson et al. (2001 ▶). We are interested in the synthesis of dithiocarbamate, pyridine-2-thionate (Yih et al., 2010 ▶) and N,N-dimethyldithiocarbarmoyl (Yih & Lee, 2010 ▶) metal complexes. For a phenoxythiocarbonyl–palladium complex, see: Yih & Lee (2004 ▶). For C—H⋯O interactions, see: Strasser et al. (2009 ▶); Arumugam et al. (2010 ▶). For C—H⋯π interactions, see: Suresh et al. (2007 ▶). For π–π interactions, see: Bartholomä et al. (2009) ▶; Hu et al. (2009 ▶). For the C—H⋯Cl interactions, see: Shawkataly et al. (2010 ▶); Qi et al. (2009 ▶). For C—H⋯S interactions, see: Asad et al. (2010 ▶); Goh et al. (2010 ▶). For C–H⋯acceptor interactions, see: Steiner (1996 ▶). For typical C—O and C—S bond lengths, see: Huheey (1983 ▶). For Mo—CO and C—O bond lengths in other molybdenum–carbonyl complexes, see: Yih & Lee (2008 ▶) and references therein.
Experimental
Crystal data
[Mo(C7H5OS)Cl(C18H15P)2(CO)2]
M r = 849.12
Triclinic,

a = 10.5685 (10) Å
b = 12.5224 (11) Å
c = 16.3983 (14) Å
α = 82.088 (2)°
β = 77.476 (2)°
γ = 67.212 (2)°
V = 1949.7 (3) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.58 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.16 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.913, T max = 0.944
25423 measured reflections
8942 independent reflections
6714 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.075
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.053
wR(F 2) = 0.128
S = 1.00
8942 reflections
478 parameters
3 restraints
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 1.02 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.81 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810052530/bg2377sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810052530/bg2377Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1, Cg2, Cg3 and Cg7 are the centroids of the C4–C9, C10–C15, C16–C21 and C40–C45 rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C23—H23⋯O3 | 0.95 | 2.31 | 3.208 (5) | 157 |
| C24—H24⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.199 (5) | 123 |
| C39—H39⋯Cl1 | 0.95 | 2.80 | 3.573 (4) | 139 |
| C9—H9⋯Cg3 | 0.95 | 2.97 | 3.896 (5) | 165 |
| C14—H14⋯Cg7ii | 0.95 | 2.83 | 3.663 (5) | 147 |
| C20—H20⋯Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.97 | 3.802 (4) | 147 |
| C27—H27⋯Cg2 | 0.95 | 2.84 | 3.636 (5) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Science Council of the Republic of China for financial support (NSC98–2113-M-241–011-MY2).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The interest in the M—C(S)OPh moiety is due to its analogy with metallocarboxylic acid esters (M—C(O)OR) and metallocarboxylic acids themselves. Metallocarboxylic acids have been proposed to be the key intermediates in the homogeneous catalysis of the water gas shift reaction (Yoshida et al., 1978). O-Aryl thiocarbonate (Chen et al., 1978), benzoxazoline-2-thione (McFarlane et al., 1998), chromene-2-thione (Zheng et al., 2006), and N,N-dimethylthiocarbamate (Zhang et al., 2004) metal complexes have been reported but few phenoxylcarbonyl metal complexes have been studied (Anderson et al., 2001). We are interested in the synthesis of dithiocarbamate, pyridine-2-thionate (Yih et al., 2010) and N,N-dimethyldithiocarbarmoyl (Yih & Lee, 2010) metal complexes. To our knowledge, no chelating phenoxythiocarbonyl crystal structure has been described so far.
The molecular structure of the title compound [Mo(CO)2(SCOPh)(PPh3)2Cl], (I),is shown in Fig. 1. The geometry around the metal atom is midway a capped trigonal prism and a capped octahedron. The capped trigonal prism consist of a phosphorus atom, P2, in the unique capping position [Mo1—P2 = 2.5509 (10) Å]. Two carbonyl groups, C1-O1 and C2-O2, Cl1, and the sulfur atom S1 of the phenoxythiocarbonyl ligand are present in the capped quadrilateral face [Mo—C1 = 1.938 (4) Å; Mo—C2 = 1.998 (4) Å; Mo—Cl1 = 2.5160 (9) Å; Mo—S1 = 2.6553 (10) Å] and the phenoxythiocarbonyl ligand is at the unique edge [Mo—S1 = 2.6553 (10) Å; Mo—C3 = 2.025 (4) Å]. In contrast the capped octahedron is made up of C3 in the capping position, C1, S1, and P2 in the capped face, and P1, C2, and Cl1 in the uncapped face. Two PPh3 ligands are in trans position: P1—Mo—P2, 173.19 (3)°, while the sulfur atom of the phenoxythiocarbonyl ligand, chloride and two carbonyl groups are trans to each other: C2—Mo—S1, 170.67 (11)°, C1—Mo—Cl1, 154.93 (12)°. The mean Mo—C—O angle of (I) ( 176.4 (3)° ) shows the group to be essentially linear, similarly to other terminal carbonyls of Mo. The Mo—CO (1.938 (4), 1.998 (4) Å) and C—O (1.163 (4), 1.146 (4) Å) distances are both consistent with the range of values reported for the other molybdenum carbonyl complexes (Yih & Lee, 2008 and references therein). The Mo—C1 bond distance is clearly shorter than that of Mo—C2 due to the larger trans influence of the sulfur atom of phenoxythiocarbonyl ligand than that of the chlorine ligand.
Within the SCOPh ligand, the C—S (1.650 (4) Å) and SC—O (1.319 (4) Å) bond distances are typical for C—O and C—S bonds having partial double bond character and are certainly much shorter than typical C—O (1.43 Å) and C—S (1.82 Å) single bonds (Huheey, 1983). The S1—C3—O3 group shows a geometrical environment characteristic of sp2 hybridization of the carbon atom. In addition, the S1—C3—O3 angle of 129.0 (3)° is larger than that found in the palladium phenoxythiocarbonyl complex (125.2 (6)°) (Yih et al., 2004). To our knowledge, the title complex is the first chelating phenoxythiocarbonyl-metal complex in the literature.
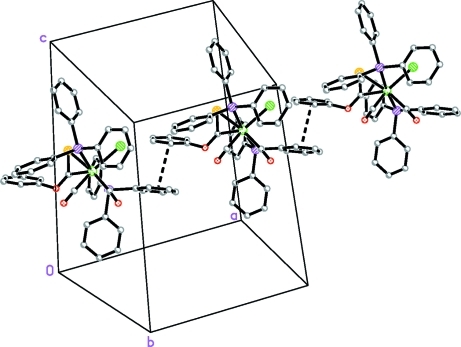
Three weak intramolecular hydrogen bonds and one intermolecular hydrogen bond are present in the structure (Table 1, entries 1-4). In addition, the phenyl ring (C4—C9) of the phenoxythiocarbonyl ligand and a phenyl ring (C10—C15) from the triphenylphosphane are nearly parallel, with an intercentroid distance of 3.938 (3)Å and a shortest inter-ring distance of 3.160 (2) Å. The resulting π-π interaction links molecules into a 1-D chain structure (Fig. 2).Finally, a supramolecular aggregation is determined by four C—H···π(arene) hydrogen bonds (Fig. 3 and Table 1, entries 5-8). The structure also presents some short CO···π(arene) contacts, O1···Cg5: 3.485 (4) and O2···Cg2iv:3.722 (3)Å, ( iv = -x + 2,-y_2,-z + 1)
In the 1H NMR spectrum of (I), 35 protons of the seven phenyl exhibit multiple resonances in the region of δ 7.12–7.73. In the 13C{1H} NMR spectrum of (I), two triplet resonances appear at δ 229.3 and δ 238.6 with 2JP—C = 12.95, 11.95 Hz couplings for the two inequivalent carbonyl groups, respectively. The 31P{1H} NMR spectrum of (I) shows one resonance at δ 34.2.
It is also noted that the IR spectrum of the title complex (I) shows four stretching bands, two at 1965, 1891 cm-1 for C=O and two at 1483, 1434 cm-1 for C-OPh groups. In the FAB mass spectra, the base peak with the typical Mo isotope distribution is in agreement with the [M+] molecular mass of (I).
Experimental
The synthesis of the title compound (I) was carried out as follows. PhOCSCl (0.135 g, 1.1 mmol) was added to a flask (100 ml) containing CH2Cl2 (10 ml) and [Mo(CH3CN)2(CO)2(PPh3)2] (0.758 g, 1.0 mmol) at room temperature. The color of the solution was changed from yellow to red immediately. The solution was concentrated under vacuum and n-hexane (10 ml) was added to initiate a yellow-brown precipitation. The resulting bright-yellow solid was isolated by filtration (G4), washed with diethyl ether (2 x 10 ml) and subsequently dried under vacuum, yielding [Mo(CO)2(SCOPh)(PPh3)2Cl] (0.764 g, 90%). Further purification was accomplished by recrystallization from 1/10 CH2Cl2/n-hexane. The orange crystals of (I) for X-ray structure analysis were obtained by slow diffusion of n-hexane into the CH2Cl2 solution of the title compound at room temperature for 3 days. Spectroscopic analysis: 1H NMR (CDCl3, 298 K, δ, p.p.m.): δ 7.12–7.73 (m, 35H, Ph). 31P{1H} NMR (CDCl3, 298 K, δ, p.p.m.): δ 34.3. 13C{1H} NMR (CDCl3, 298 K, δ, p.p.m.): δ 127.9- 134.2 (m, C of Ph), 159.7 (s, O—Ph), 229.3, 238.6 (t, CO, 2JP—C = 12.95, 11.95 Hz). MS (m/z): 850 (M+). Anal. Calcd for C45H35ClO3P2SMo: C, 63.65; H, 4.16. Found: C, 63.50; H, 4.05.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.95Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.2 times Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), with atom labels and the 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
The packing diagram of (I), showing the π-π interaction and 1-D chain structure.
Fig. 3.
The packing diagram of (I), showing the intermolecular C—H···O, C—H···π(arene) hydrogen bonds and CO···π(arene) interactions.
Crystal data
| [Mo(C7H5OS)Cl(C18H15P)2(CO)2] | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 849.12 | F(000) = 868 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.446 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.5685 (10) Å | Cell parameters from 2285 reflections |
| b = 12.5224 (11) Å | θ = 2.2–20.7° |
| c = 16.3983 (14) Å | µ = 0.58 mm−1 |
| α = 82.088 (2)° | T = 150 K |
| β = 77.476 (2)° | Block, orange |
| γ = 67.212 (2)° | 0.16 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm |
| V = 1949.7 (3) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 8942 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 6714 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.075 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 1.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.913, Tmax = 0.944 | k = −16→16 |
| 25423 measured reflections | l = −21→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.053 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.128 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.00 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0566P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 8942 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 478 parameters | Δρmax = 1.02 e Å−3 |
| 3 restraints | Δρmin = −0.81 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Mo1 | 0.77982 (3) | 0.84316 (3) | 0.741327 (19) | 0.01739 (10) | |
| Cl1 | 1.00258 (9) | 0.78068 (8) | 0.79778 (6) | 0.0237 (2) | |
| P1 | 0.77983 (9) | 1.04763 (8) | 0.71651 (6) | 0.0187 (2) | |
| P2 | 0.80792 (10) | 0.63059 (8) | 0.77147 (6) | 0.0218 (2) | |
| S1 | 0.61369 (10) | 0.87871 (8) | 0.88984 (6) | 0.0247 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.6626 (4) | 0.8368 (3) | 0.6676 (2) | 0.0246 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.8831 (4) | 0.8414 (3) | 0.6237 (2) | 0.0259 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.5806 (4) | 0.9314 (3) | 0.7956 (2) | 0.0212 (8) | |
| C4 | 0.3344 (4) | 1.0250 (3) | 0.8332 (2) | 0.0261 (9) | |
| C5 | 0.2484 (4) | 0.9681 (3) | 0.8282 (2) | 0.0284 (9) | |
| H5 | 0.2768 | 0.9084 | 0.7905 | 0.034* | |
| C6 | 0.1185 (4) | 1.0009 (4) | 0.8801 (3) | 0.0338 (10) | |
| H6 | 0.0563 | 0.9636 | 0.8782 | 0.041* | |
| C7 | 0.0797 (4) | 1.0870 (4) | 0.9344 (3) | 0.0381 (10) | |
| H7 | −0.0100 | 1.1102 | 0.9688 | 0.046* | |
| C8 | 0.1699 (5) | 1.1401 (4) | 0.9392 (3) | 0.0389 (11) | |
| H8 | 0.1431 | 1.1980 | 0.9780 | 0.047* | |
| C9 | 0.3002 (4) | 1.1094 (4) | 0.8875 (3) | 0.0337 (10) | |
| H9 | 0.3631 | 1.1458 | 0.8899 | 0.040* | |
| C10 | 0.9438 (4) | 1.0723 (3) | 0.6985 (2) | 0.0213 (8) | |
| C11 | 1.0648 (4) | 0.9969 (3) | 0.6529 (2) | 0.0260 (8) | |
| H11 | 1.0672 | 0.9253 | 0.6382 | 0.031* | |
| C12 | 1.1829 (4) | 1.0261 (4) | 0.6287 (3) | 0.0362 (10) | |
| H12 | 1.2651 | 0.9746 | 0.5970 | 0.043* | |
| C13 | 1.1808 (4) | 1.1293 (4) | 0.6504 (3) | 0.0367 (10) | |
| H13 | 1.2611 | 1.1491 | 0.6332 | 0.044* | |
| C14 | 1.0628 (4) | 1.2033 (4) | 0.6969 (3) | 0.0390 (11) | |
| H14 | 1.0618 | 1.2738 | 0.7129 | 0.047* | |
| C15 | 0.9447 (4) | 1.1748 (3) | 0.7206 (3) | 0.0317 (9) | |
| H15 | 0.8631 | 1.2265 | 0.7526 | 0.038* | |
| C16 | 0.6791 (4) | 1.1418 (3) | 0.8016 (2) | 0.0190 (7) | |
| C17 | 0.5762 (4) | 1.2503 (3) | 0.7907 (2) | 0.0257 (8) | |
| H17 | 0.5522 | 1.2773 | 0.7370 | 0.031* | |
| C18 | 0.5087 (4) | 1.3192 (3) | 0.8585 (3) | 0.0319 (9) | |
| H18 | 0.4391 | 1.3936 | 0.8506 | 0.038* | |
| C19 | 0.5411 (4) | 1.2812 (3) | 0.9366 (2) | 0.0296 (9) | |
| H19 | 0.4936 | 1.3285 | 0.9827 | 0.036* | |
| C20 | 0.6439 (4) | 1.1730 (3) | 0.9479 (2) | 0.0269 (9) | |
| H20 | 0.6674 | 1.1465 | 1.0017 | 0.032* | |
| C21 | 0.7121 (4) | 1.1037 (3) | 0.8810 (2) | 0.0233 (8) | |
| H21 | 0.7820 | 1.0296 | 0.8893 | 0.028* | |
| C22 | 0.7063 (4) | 1.1261 (3) | 0.6235 (2) | 0.0208 (8) | |
| C23 | 0.5875 (4) | 1.1172 (3) | 0.6072 (2) | 0.0258 (8) | |
| H23 | 0.5432 | 1.0723 | 0.6451 | 0.031* | |
| C24 | 0.5325 (4) | 1.1720 (3) | 0.5373 (2) | 0.0292 (9) | |
| H24 | 0.4511 | 1.1644 | 0.5274 | 0.035* | |
| C25 | 0.5952 (4) | 1.2384 (3) | 0.4810 (2) | 0.0293 (9) | |
| H25 | 0.5569 | 1.2767 | 0.4328 | 0.035* | |
| C26 | 0.7136 (4) | 1.2480 (4) | 0.4960 (3) | 0.0349 (10) | |
| H26 | 0.7577 | 1.2925 | 0.4577 | 0.042* | |
| C27 | 0.7684 (4) | 1.1931 (3) | 0.5667 (2) | 0.0298 (9) | |
| H27 | 0.8495 | 1.2011 | 0.5766 | 0.036* | |
| C28 | 0.6717 (4) | 0.5957 (3) | 0.7413 (2) | 0.0262 (9) | |
| C29 | 0.6950 (5) | 0.5153 (3) | 0.6840 (3) | 0.0330 (10) | |
| H29 | 0.7876 | 0.4705 | 0.6591 | 0.040* | |
| C30 | 0.5822 (6) | 0.5006 (4) | 0.6631 (3) | 0.0454 (13) | |
| H30 | 0.5983 | 0.4467 | 0.6229 | 0.054* | |
| C31 | 0.4482 (6) | 0.5630 (4) | 0.6998 (3) | 0.0488 (14) | |
| H31 | 0.3720 | 0.5528 | 0.6846 | 0.059* | |
| C32 | 0.4239 (5) | 0.6405 (4) | 0.7588 (3) | 0.0418 (12) | |
| H32 | 0.3313 | 0.6822 | 0.7853 | 0.050* | |
| C33 | 0.5353 (4) | 0.6575 (4) | 0.7793 (3) | 0.0333 (10) | |
| H33 | 0.5185 | 0.7115 | 0.8195 | 0.040* | |
| C34 | 0.8098 (4) | 0.5616 (3) | 0.8780 (2) | 0.0250 (8) | |
| C35 | 0.7853 (5) | 0.4590 (4) | 0.8978 (3) | 0.0403 (11) | |
| H35 | 0.7664 | 0.4240 | 0.8563 | 0.048* | |
| C36 | 0.7882 (5) | 0.4078 (4) | 0.9780 (3) | 0.0437 (12) | |
| H36 | 0.7733 | 0.3368 | 0.9908 | 0.052* | |
| C37 | 0.8122 (4) | 0.4579 (4) | 1.0391 (3) | 0.0352 (10) | |
| H37 | 0.8138 | 0.4223 | 1.0941 | 0.042* | |
| C38 | 0.8340 (4) | 0.5609 (4) | 1.0196 (2) | 0.0317 (9) | |
| H38 | 0.8488 | 0.5972 | 1.0619 | 0.038* | |
| C39 | 0.8346 (4) | 0.6120 (3) | 0.9393 (2) | 0.0267 (8) | |
| H39 | 0.8522 | 0.6819 | 0.9264 | 0.032* | |
| C40 | 0.9734 (4) | 0.5414 (3) | 0.7104 (3) | 0.0301 (9) | |
| C41 | 1.0837 (4) | 0.4694 (4) | 0.7479 (3) | 0.0394 (11) | |
| H41 | 1.0720 | 0.4585 | 0.8072 | 0.047* | |
| C42 | 1.2122 (5) | 0.4129 (4) | 0.6989 (4) | 0.0572 (16) | |
| H42 | 1.2880 | 0.3632 | 0.7251 | 0.069* | |
| C43 | 1.2308 (6) | 0.4275 (5) | 0.6144 (4) | 0.0636 (18) | |
| H43 | 1.3191 | 0.3879 | 0.5816 | 0.076* | |
| C44 | 1.1228 (6) | 0.4992 (5) | 0.5763 (4) | 0.0601 (16) | |
| H44 | 1.1361 | 0.5092 | 0.5169 | 0.072* | |
| C45 | 0.9937 (5) | 0.5577 (4) | 0.6235 (3) | 0.0417 (11) | |
| H45 | 0.9194 | 0.6087 | 0.5967 | 0.050* | |
| O1 | 0.5958 (3) | 0.8323 (3) | 0.62133 (18) | 0.0408 (8) | |
| O2 | 0.9334 (3) | 0.8416 (3) | 0.55439 (18) | 0.0425 (8) | |
| O3 | 0.4605 (3) | 0.9978 (2) | 0.77308 (16) | 0.0340 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Mo1 | 0.01565 (16) | 0.02145 (17) | 0.01619 (16) | −0.00996 (12) | −0.00020 (11) | 0.00036 (12) |
| Cl1 | 0.0189 (4) | 0.0264 (5) | 0.0288 (5) | −0.0124 (4) | −0.0075 (4) | 0.0054 (4) |
| P1 | 0.0146 (4) | 0.0212 (5) | 0.0189 (5) | −0.0077 (4) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0003 (4) |
| P2 | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0220 (5) | 0.0231 (5) | −0.0111 (4) | −0.0021 (4) | −0.0015 (4) |
| S1 | 0.0223 (5) | 0.0310 (5) | 0.0189 (4) | −0.0107 (4) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0018 (4) |
| C1 | 0.025 (2) | 0.034 (2) | 0.0206 (19) | −0.0184 (17) | −0.0052 (14) | 0.0052 (16) |
| C2 | 0.026 (2) | 0.033 (2) | 0.0200 (13) | −0.0162 (17) | 0.0028 (13) | −0.0023 (16) |
| C3 | 0.0212 (19) | 0.0235 (19) | 0.0226 (19) | −0.0149 (16) | −0.0007 (15) | 0.0014 (15) |
| C4 | 0.0122 (17) | 0.039 (2) | 0.022 (2) | −0.0074 (16) | 0.0004 (15) | 0.0017 (17) |
| C5 | 0.023 (2) | 0.033 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0094 (17) | −0.0037 (17) | −0.0026 (17) |
| C6 | 0.023 (2) | 0.047 (3) | 0.034 (2) | −0.020 (2) | −0.0021 (18) | 0.002 (2) |
| C7 | 0.023 (2) | 0.048 (3) | 0.037 (3) | −0.014 (2) | 0.0089 (19) | −0.005 (2) |
| C8 | 0.040 (3) | 0.037 (2) | 0.040 (3) | −0.017 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.012 (2) |
| C9 | 0.029 (2) | 0.042 (3) | 0.035 (2) | −0.022 (2) | 0.0000 (18) | −0.0013 (19) |
| C10 | 0.0200 (19) | 0.0242 (19) | 0.0209 (19) | −0.0115 (16) | −0.0033 (15) | 0.0044 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0203 (19) | 0.033 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.0147 (17) | 0.0024 (16) | −0.0052 (17) |
| C12 | 0.021 (2) | 0.043 (3) | 0.039 (3) | −0.0114 (19) | 0.0069 (18) | −0.006 (2) |
| C13 | 0.027 (2) | 0.044 (3) | 0.043 (3) | −0.024 (2) | 0.0030 (19) | 0.005 (2) |
| C14 | 0.034 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.056 (3) | −0.021 (2) | 0.002 (2) | −0.006 (2) |
| C15 | 0.021 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.043 (3) | −0.0130 (17) | 0.0035 (18) | −0.0036 (18) |
| C16 | 0.0162 (17) | 0.0236 (19) | 0.0172 (18) | −0.0119 (15) | 0.0047 (14) | −0.0001 (14) |
| C17 | 0.022 (2) | 0.025 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.0099 (16) | 0.0016 (16) | 0.0030 (16) |
| C18 | 0.027 (2) | 0.026 (2) | 0.035 (2) | −0.0070 (17) | 0.0031 (18) | −0.0023 (18) |
| C19 | 0.029 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.0135 (18) | 0.0081 (17) | −0.0092 (17) |
| C20 | 0.025 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.0205 (19) | −0.0168 (18) | 0.0035 (16) | −0.0015 (17) |
| C21 | 0.0209 (19) | 0.0223 (19) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0113 (16) | −0.0017 (16) | 0.0010 (16) |
| C22 | 0.0177 (18) | 0.0218 (19) | 0.0194 (18) | −0.0062 (15) | 0.0018 (14) | −0.0017 (15) |
| C23 | 0.0180 (19) | 0.032 (2) | 0.026 (2) | −0.0099 (16) | −0.0023 (16) | 0.0037 (17) |
| C24 | 0.023 (2) | 0.034 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0105 (18) | −0.0026 (17) | 0.0015 (17) |
| C25 | 0.036 (2) | 0.029 (2) | 0.0159 (19) | −0.0071 (18) | −0.0046 (17) | 0.0042 (16) |
| C26 | 0.039 (3) | 0.036 (2) | 0.030 (2) | −0.021 (2) | −0.0022 (19) | 0.0094 (19) |
| C27 | 0.027 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.0164 (18) | 0.0008 (17) | 0.0050 (17) |
| C28 | 0.033 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.024 (2) | −0.0200 (18) | −0.0096 (17) | 0.0094 (16) |
| C29 | 0.046 (3) | 0.031 (2) | 0.033 (2) | −0.025 (2) | −0.013 (2) | 0.0047 (18) |
| C30 | 0.074 (4) | 0.042 (3) | 0.041 (3) | −0.040 (3) | −0.029 (3) | 0.015 (2) |
| C31 | 0.068 (4) | 0.049 (3) | 0.056 (3) | −0.048 (3) | −0.039 (3) | 0.030 (3) |
| C32 | 0.036 (3) | 0.044 (3) | 0.054 (3) | −0.027 (2) | −0.016 (2) | 0.018 (2) |
| C33 | 0.033 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.038 (2) | −0.022 (2) | −0.0061 (19) | 0.0023 (19) |
| C34 | 0.023 (2) | 0.025 (2) | 0.025 (2) | −0.0087 (16) | −0.0032 (16) | −0.0002 (16) |
| C35 | 0.054 (3) | 0.035 (2) | 0.041 (3) | −0.024 (2) | −0.017 (2) | 0.008 (2) |
| C36 | 0.052 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.048 (3) | −0.027 (2) | −0.013 (2) | 0.019 (2) |
| C37 | 0.031 (2) | 0.040 (3) | 0.030 (2) | −0.013 (2) | −0.0043 (19) | 0.0127 (19) |
| C38 | 0.028 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.024 (2) | −0.0104 (19) | −0.0035 (17) | −0.0001 (18) |
| C39 | 0.022 (2) | 0.026 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0077 (16) | −0.0016 (16) | 0.0017 (16) |
| C40 | 0.030 (2) | 0.029 (2) | 0.035 (2) | −0.0169 (18) | 0.0023 (18) | −0.0126 (18) |
| C41 | 0.024 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.062 (3) | −0.0143 (19) | −0.005 (2) | −0.015 (2) |
| C42 | 0.026 (2) | 0.042 (3) | 0.112 (5) | −0.017 (2) | −0.002 (3) | −0.030 (3) |
| C43 | 0.037 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.102 (5) | −0.027 (3) | 0.032 (3) | −0.046 (3) |
| C44 | 0.066 (4) | 0.056 (3) | 0.061 (4) | −0.039 (3) | 0.036 (3) | −0.037 (3) |
| C45 | 0.048 (3) | 0.039 (3) | 0.038 (3) | −0.023 (2) | 0.011 (2) | −0.012 (2) |
| O1 | 0.052 (2) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0298 (17) | −0.0332 (17) | −0.0188 (15) | 0.0068 (14) |
| O2 | 0.0468 (19) | 0.059 (2) | 0.0250 (16) | −0.0300 (16) | 0.0082 (14) | −0.0066 (14) |
| O3 | 0.0160 (14) | 0.0525 (18) | 0.0246 (15) | −0.0089 (13) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0103 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Mo1—C1 | 1.938 (4) | C20—C21 | 1.381 (5) |
| Mo1—C2 | 1.998 (4) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| Mo1—C3 | 2.025 (4) | C21—H21 | 0.9500 |
| Mo1—Cl1 | 2.5160 (9) | C22—C23 | 1.387 (5) |
| Mo1—P1 | 2.5368 (10) | C22—C27 | 1.397 (5) |
| Mo1—P2 | 2.5509 (10) | C23—C24 | 1.373 (5) |
| Mo1—S1 | 2.6553 (10) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| P1—C16 | 1.819 (4) | C24—C25 | 1.391 (5) |
| P1—C10 | 1.831 (4) | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| P1—C22 | 1.845 (4) | C25—C26 | 1.378 (6) |
| P2—C40 | 1.829 (4) | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| P2—C28 | 1.834 (4) | C26—C27 | 1.383 (5) |
| P2—C34 | 1.840 (4) | C26—H26 | 0.9500 |
| S1—C3 | 1.650 (4) | C27—H27 | 0.9500 |
| C1—O1 | 1.163 (4) | C28—C29 | 1.388 (5) |
| C2—O2 | 1.146 (4) | C28—C33 | 1.394 (6) |
| C3—O3 | 1.319 (4) | C29—C30 | 1.392 (6) |
| C4—C9 | 1.365 (6) | C29—H29 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.375 (5) | C30—C31 | 1.372 (7) |
| C4—O3 | 1.427 (4) | C30—H30 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.390 (5) | C31—C32 | 1.379 (7) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C31—H31 | 0.9500 |
| C6—C7 | 1.374 (6) | C32—C33 | 1.389 (5) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C32—H32 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C8 | 1.376 (6) | C33—H33 | 0.9500 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C34—C39 | 1.377 (5) |
| C8—C9 | 1.392 (6) | C34—C35 | 1.390 (5) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C35—C36 | 1.382 (6) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9500 | C35—H35 | 0.9500 |
| C10—C15 | 1.385 (5) | C36—C37 | 1.367 (6) |
| C10—C11 | 1.389 (5) | C36—H36 | 0.9500 |
| C11—C12 | 1.395 (5) | C37—C38 | 1.380 (6) |
| C11—H11 | 0.9500 | C37—H37 | 0.9500 |
| C12—C13 | 1.378 (6) | C38—C39 | 1.383 (5) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9500 | C38—H38 | 0.9500 |
| C13—C14 | 1.372 (6) | C39—H39 | 0.9500 |
| C13—H13 | 0.9500 | C40—C41 | 1.377 (6) |
| C14—C15 | 1.391 (5) | C40—C45 | 1.392 (6) |
| C14—H14 | 0.9500 | C41—C42 | 1.389 (6) |
| C15—H15 | 0.9500 | C41—H41 | 0.9500 |
| C16—C17 | 1.391 (5) | C42—C43 | 1.354 (8) |
| C16—C21 | 1.393 (5) | C42—H42 | 0.9500 |
| C17—C18 | 1.391 (5) | C43—C44 | 1.364 (8) |
| C17—H17 | 0.9500 | C43—H43 | 0.9500 |
| C18—C19 | 1.372 (5) | C44—C45 | 1.386 (6) |
| C18—H18 | 0.9500 | C44—H44 | 0.9500 |
| C19—C20 | 1.388 (5) | C45—H45 | 0.9500 |
| C19—H19 | 0.9500 | ||
| C1—Mo1—C2 | 71.73 (15) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.6 |
| C1—Mo1—C3 | 73.73 (15) | C18—C19—C20 | 119.5 (4) |
| C2—Mo1—C3 | 132.98 (15) | C18—C19—H19 | 120.3 |
| C1—Mo1—Cl1 | 154.93 (12) | C20—C19—H19 | 120.3 |
| C2—Mo1—Cl1 | 91.25 (11) | C21—C20—C19 | 120.3 (4) |
| C3—Mo1—Cl1 | 130.01 (10) | C21—C20—H20 | 119.9 |
| C1—Mo1—P1 | 104.78 (11) | C19—C20—H20 | 119.9 |
| C2—Mo1—P1 | 78.19 (11) | C20—C21—C16 | 120.4 (3) |
| C3—Mo1—P1 | 80.87 (10) | C20—C21—H21 | 119.8 |
| Cl1—Mo1—P1 | 88.95 (3) | C16—C21—H21 | 119.8 |
| C1—Mo1—P2 | 81.36 (11) | C23—C22—C27 | 117.9 (3) |
| C2—Mo1—P2 | 101.33 (11) | C23—C22—P1 | 119.9 (3) |
| C3—Mo1—P2 | 103.97 (10) | C27—C22—P1 | 122.2 (3) |
| Cl1—Mo1—P2 | 84.26 (3) | C24—C23—C22 | 121.3 (4) |
| P1—Mo1—P2 | 173.19 (3) | C24—C23—H23 | 119.3 |
| C1—Mo1—S1 | 104.16 (11) | C22—C23—H23 | 119.3 |
| C2—Mo1—S1 | 170.67 (11) | C23—C24—C25 | 120.4 (4) |
| C3—Mo1—S1 | 38.38 (10) | C23—C24—H24 | 119.8 |
| Cl1—Mo1—S1 | 95.19 (3) | C25—C24—H24 | 119.8 |
| P1—Mo1—S1 | 95.15 (3) | C26—C25—C24 | 119.1 (4) |
| P2—Mo1—S1 | 86.06 (3) | C26—C25—H25 | 120.4 |
| C16—P1—C10 | 100.80 (16) | C24—C25—H25 | 120.4 |
| C16—P1—C22 | 104.60 (16) | C25—C26—C27 | 120.4 (4) |
| C10—P1—C22 | 101.17 (16) | C25—C26—H26 | 119.8 |
| C16—P1—Mo1 | 114.53 (11) | C27—C26—H26 | 119.8 |
| C10—P1—Mo1 | 120.45 (12) | C26—C27—C22 | 120.9 (4) |
| C22—P1—Mo1 | 113.17 (12) | C26—C27—H27 | 119.5 |
| C40—P2—C28 | 106.39 (18) | C22—C27—H27 | 119.5 |
| C40—P2—C34 | 104.36 (18) | C29—C28—C33 | 119.2 (4) |
| C28—P2—C34 | 100.80 (17) | C29—C28—P2 | 125.1 (3) |
| C40—P2—Mo1 | 108.48 (13) | C33—C28—P2 | 115.7 (3) |
| C28—P2—Mo1 | 113.81 (12) | C28—C29—C30 | 119.7 (4) |
| C34—P2—Mo1 | 121.70 (12) | C28—C29—H29 | 120.1 |
| C3—S1—Mo1 | 49.67 (13) | C30—C29—H29 | 120.1 |
| O1—C1—Mo1 | 177.8 (3) | C31—C30—C29 | 120.7 (5) |
| O2—C2—Mo1 | 175.0 (3) | C31—C30—H30 | 119.6 |
| O3—C3—S1 | 129.0 (3) | C29—C30—H30 | 119.6 |
| O3—C3—Mo1 | 138.8 (3) | C30—C31—C32 | 120.1 (4) |
| S1—C3—Mo1 | 91.95 (16) | C30—C31—H31 | 120.0 |
| C9—C4—C5 | 123.6 (4) | C32—C31—H31 | 120.0 |
| C9—C4—O3 | 120.1 (3) | C31—C32—C33 | 119.8 (5) |
| C5—C4—O3 | 116.1 (3) | C31—C32—H32 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 117.7 (4) | C33—C32—H32 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 121.2 | C32—C33—C28 | 120.4 (4) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 121.2 | C32—C33—H33 | 119.8 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.2 (4) | C28—C33—H33 | 119.8 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.9 | C39—C34—C35 | 119.2 (4) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.9 | C39—C34—P2 | 120.0 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.5 (4) | C35—C34—P2 | 120.7 (3) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.7 | C36—C35—C34 | 120.0 (4) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.7 | C36—C35—H35 | 120.0 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.4 (4) | C34—C35—H35 | 120.0 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.8 | C37—C36—C35 | 120.9 (4) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.8 | C37—C36—H36 | 119.5 |
| C4—C9—C8 | 117.6 (4) | C35—C36—H36 | 119.5 |
| C4—C9—H9 | 121.2 | C36—C37—C38 | 119.0 (4) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 121.2 | C36—C37—H37 | 120.5 |
| C15—C10—C11 | 118.5 (3) | C38—C37—H37 | 120.5 |
| C15—C10—P1 | 120.0 (3) | C37—C38—C39 | 120.9 (4) |
| C11—C10—P1 | 121.0 (3) | C37—C38—H38 | 119.6 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 120.2 (4) | C39—C38—H38 | 119.6 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 | C34—C39—C38 | 120.0 (4) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 | C34—C39—H39 | 120.0 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 120.3 (4) | C38—C39—H39 | 120.0 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 | C41—C40—C45 | 119.0 (4) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 | C41—C40—P2 | 121.7 (3) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.1 (4) | C45—C40—P2 | 118.7 (3) |
| C14—C13—H13 | 120.0 | C40—C41—C42 | 119.8 (5) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 120.0 | C40—C41—H41 | 120.1 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 119.7 (4) | C42—C41—H41 | 120.1 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 | C43—C42—C41 | 120.9 (5) |
| C15—C14—H14 | 120.1 | C43—C42—H42 | 119.5 |
| C10—C15—C14 | 121.2 (4) | C41—C42—H42 | 119.5 |
| C10—C15—H15 | 119.4 | C42—C43—C44 | 120.0 (5) |
| C14—C15—H15 | 119.4 | C42—C43—H43 | 120.0 |
| C17—C16—C21 | 119.1 (3) | C44—C43—H43 | 120.0 |
| C17—C16—P1 | 123.5 (3) | C43—C44—C45 | 120.4 (5) |
| C21—C16—P1 | 117.4 (3) | C43—C44—H44 | 119.8 |
| C18—C17—C16 | 119.8 (4) | C45—C44—H44 | 119.8 |
| C18—C17—H17 | 120.1 | C44—C45—C40 | 119.8 (5) |
| C16—C17—H17 | 120.1 | C44—C45—H45 | 120.1 |
| C19—C18—C17 | 120.9 (4) | C40—C45—H45 | 120.1 |
| C19—C18—H18 | 119.6 | C3—O3—C4 | 120.2 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1, Cg2, Cg3 and Cg7 are the centroids of the C4–C9, C10–C15, C16–C21 and C40–C45 rings, respectively. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C23—H23···O3 | 0.95 | 2.31 | 3.208 (5) | 157 |
| C24—H24···O1i | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.199 (5) | 123 |
| C39—H39···Cl1 | 0.95 | 2.80 | 3.573 (4) | 139 |
| C39—H39···S1 | 0.95 | 2.87 | 3.361 (4) | 114 |
| C9—H9···Cg3 | 0.95 | 2.97 | 3.896 (5) | 165 |
| C14—H14···Cg7ii | 0.95 | 2.83 | 3.663 (5) | 147 |
| C20—H20···Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.97 | 3.802 (4) | 147 |
| C27—H27···Cg2 | 0.95 | 2.84 | 3.636 (5) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) x, y+1, z; (iii) −x+1, −y+2, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BG2377).
References
- Anderson, S., Cook, D. J. & Hill, A. F. (2001). Organometallics, 20, 2468–2476.
- Arumugam, N., Abdul Rahim, A. S., Osman, H., Yeap, C. S. & Fun, H.-K. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1214–o1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Asad, M., Oo, C.-W., Osman, H., Yeap, C. S. & Fun, H.-K. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2861–o2862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bartholomä, M. D., Ouellette, W. & Zubieta, J. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2007). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chen, H. W., Fackler, J. P., Schussler, D. P. & Thompson, L. D. (1978). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 100, 2370–2375.
- Goh, J. H., Fun, H.-K., Vinayaka, A. C. & Kalluraya, B. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1233–o1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.-Y., Chu, X.-W. & Qu, Z.-R. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Huheey, J. E. (1983). Inorganic Chemistry: Principles of Structure and Reactivity, 3rd ed., p. A-37. New York: Harper & Row.
- McFarlane, W., Akrivos, P. D., Aslanudis, P., Karagiannidis, P., Atzisymeon, C., Numan, M. & Kokkou, S. (1998). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 281, 121–125.
- Qi, Z.-P., Wang, A.-D., Zhang, H. & Wang, X.-X. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, m1507–m1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Shawkataly, O. bin, Khan, I. A., Yeap, C. S. & Fun, H.-K. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, m90–m91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Steiner, Th. (1996). Crystallogr. Rev 6, 1–57.
- Strasser, C. E., Cronje, S. & Raubenheimer, H. G. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, m914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Suresh, J., Kumar, R. S., Perumal, S. & Natarajan, S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o1375–o1376.
- Yih, K. H. & Lee, G. H. (2004). J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 51, 265–270.
- Yih, K. H. & Lee, G. H. (2008). J. Organomet. Chem. 693, 3303–3311.
- Yih, K. H. & Lee, G. H. (2010). Organometallics, 29, 3397–3403.
- Yih, K.-H., Wang, H.-F. & Lee, G.-H. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, m1189–m1190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T., Ueda, Y. & Otsuka, S. (1978). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 100, 3941–3942.
- Zhang, W. & Shi, M. (2004). Tetrahedron Lett. 45, 8921–8924.
- Zheng, Z., Chen, J., Luo, N., Yu, Z. & Han, X. (2006). Organometallics, 25, 5301–5310.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810052530/bg2377sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810052530/bg2377Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report