Figure 2.
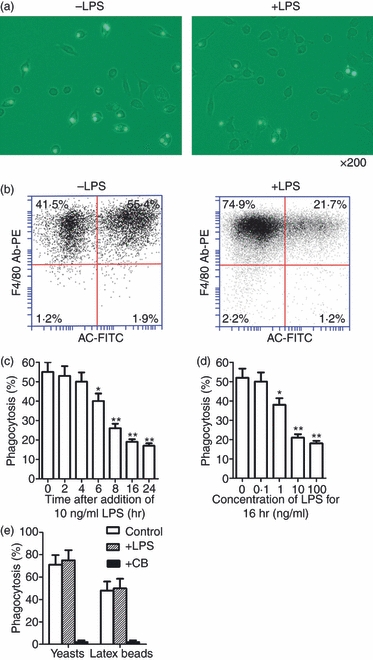
Effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils by mouse peritoneal macrophages. (a) Representative images of macrophages that have engulfed fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labelled apoptotic neutrophils. Magnification × 200. Macrophages were treated with 10 ng/ml LPS for 16 hr and assayed for phagocytic ability. (b) The macrophage phagocytic rate was quantitatively analysed by flow cytometry phagocytic macrophages were double-positive cells for PE (labeled F4/80) and FITC (labeled apoptotic cell, AC). (c, d) Time-dependent (c) and dose-dependent (d) LPS inhibition of phagocytosis by macrophages based on analysis of flow cytometry. (e) Phagocytosis of yeasts and latex beads by macrophages. Macrophages were treated with 10 ng/ml LPS for 16 hr or with 5 μg/ml cytochalasin B (CB) for 1 hr, and then co-cultured with latex beads or FITC-labelled yeasts for 30 min. Data represent the mean ± standard error of the mean for three separate experiments. *P<0·05; **P<0·01.
