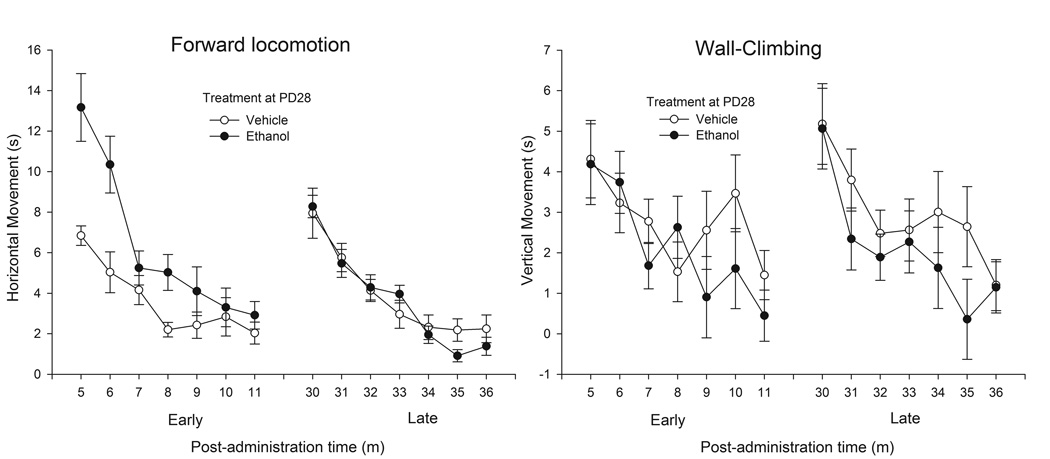
Figure 1.
Locomotor activity (forward locomotion and wall-climbing, left and right sections, respectively, expressed in seconds) in 28-day-old male and female adolescent rats as a function of ethanol treatment (0.0 [vehicle] or 2.5 g/kg) and post-administration bin of assessment (5–11 min or 30–36 min; early and late intervals, respectively). Data were collapsed across sex (male or female). The sex factor did not exert a significant main effect or significantly interact with the remaining variables. The vertical bars indicate SEM.