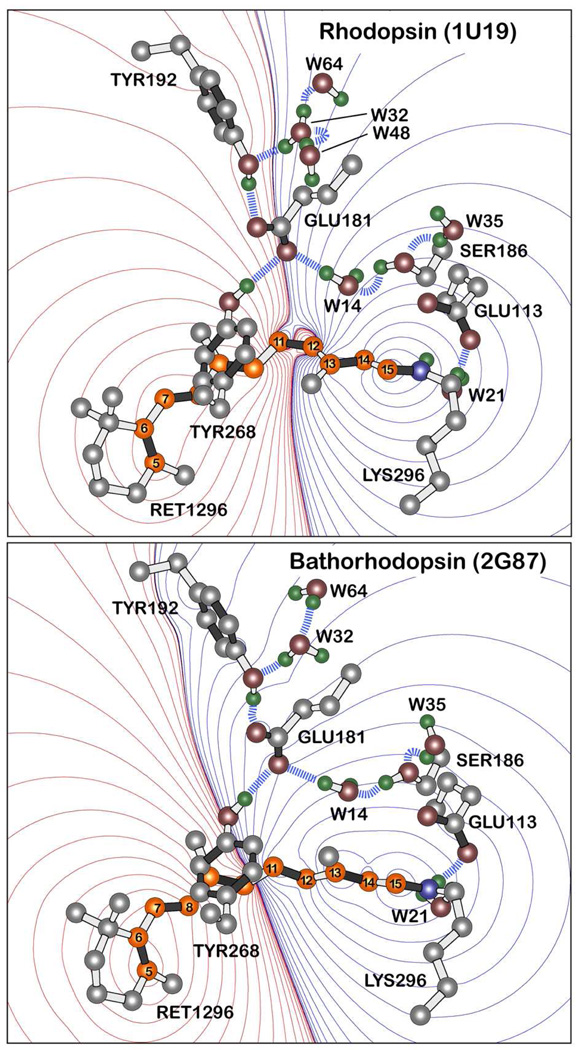
Figure 1.
Charge shifts upon excitation of the chromophore in rhodopsin (top) and bathorhodopsin (bottom) into the lowest-lying strongly allowed 1Bu+-like excited singlet states based on SAC-CISD calculations (see text). Red contours indicate regions of increased positive charge and blue contours regions of increased negative charge. Note that the carboxylate oxygen atoms of the Glu-181 residue in rhodopsin lie along the nodal line whereas in bathorhodopsin, these two atoms lie within the region of net negative charge. The contours are drawn at the following first order electrostatic energies: 0 (black), ±0.282, ±2.26, ±7.63, ±18, ±35.3, ±61, ±96.9, ±144, ±206, ±282, ±376, ±488, ±621, ±775 kJ/mol. Key hydrogen bonds are indicated with blue dashed lines, and the polyene atoms of the retinal chromophore are shown in orange and numbered following convention. The heavy atom coordinates of the binding sites were taken from the 1U192 and 2G873 crystal structures of rhodopsin and bathorhodopsin, respectively. Waters are labeled using the PDB numbers minus 2000. Only polar hydrogen atoms are shown, but all hydrogen atoms were included in the calculations and were optimized along with the chromophore by using B3LYP/6-31G(d) procedures.