Figure 1.
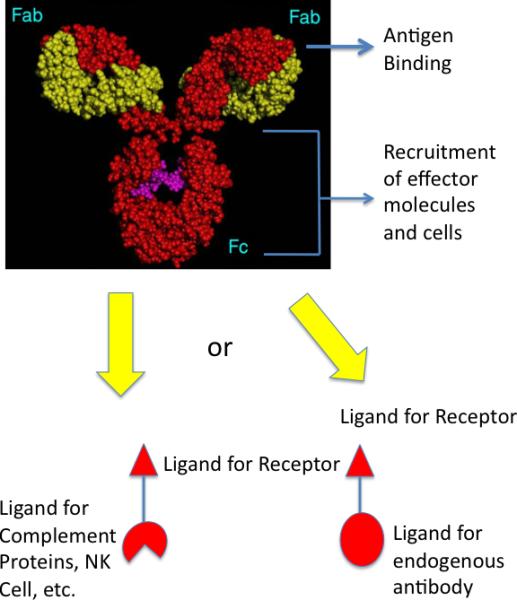
Comparison of a native IgG antibody and a hypothetical synthetic model. Native antibodies have two antigen binding pockets in their Fab regions and a constant region (Fc) capable of interacting with effector molecules and cells, such as the complement proteins, macrophages, natural killer cells, etc. Antibodies could be made by joining a high affinity and selectivity protein-binding molecule to one or more ligands for effector molecules or cells (left). Alternatively, the receptor ligand could be coupled to a molecule bound tightly by an endogenous antibody, whose Fc region would then act to recruit the effector molecules (right; also see Fig. 2)
