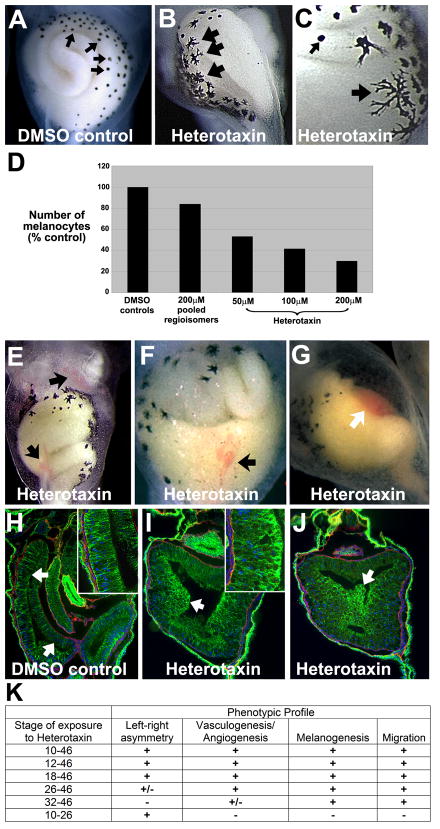
Figure 4. Heterotaxin perturbs melanogenesis, angiogenesis and cell rearrangements.
Compared to the round melanocytes seen in DMSO controls (small arrows, A, C), heterotaxin-treated embryos (two different embryos are shown in B,C) exhibit highly dendritic pigment cells (large arrows, B-C). D) Number of abdominal melanocytes in embryos exposed to either DMSO, the active pool identified in the original pilot screen, or different concentrations of purified heterotaxin. E-G) Heterotaxin induces mild (arrows, E, F) to severe (arrow, G) defects in vasculogenesis (compare the three different examples in E-G to DMSO control in A). H-J) Immunohistochemical staining for E-cadherin, (green), laminin (red) and nuclei (blue; DAPI) on frontal sections (100X) through the gut tube of embryos treated with DMSO (H, control), 100μM heterotaxin (I) or 200μM heterotaxin (J). A single-layer columnar epithelium lines the digestive tract of the DMSO tadpole (arrows, H; inset at 400X), while the cells lining the heterotaxin-treated gut are round, exhibit high levels of E-cadherin (green), and have failed to rearrange into a single layer [arrows, I (inset at 400X), J]. K) Time course studies reveal the sensitivity of each phenotype to heterotaxin exposure. “Left-right asymmetry” = reversal of heart looping, foregut looping, and/or intestinal rotation; Vasculogenesis/Angiogenesis” = hemorrhaging or enlarged blood vessels; “Melanogenesis” = decreased number and increased dendricity of melanocytes; “migration” = perturbed cell rearrangement, indicated by shortening of the primitive gut tube. “+” indicates that at least 75% of embryos exhibited the phenotype in two or more independent trials; “+/−“ indicates that at least 50% of embryos exhibited the phenotype in two or more independent trials. (See Figure S1 for a similar phenotypic profile induced by a known TGF-β inhibitor, SB-505124.)