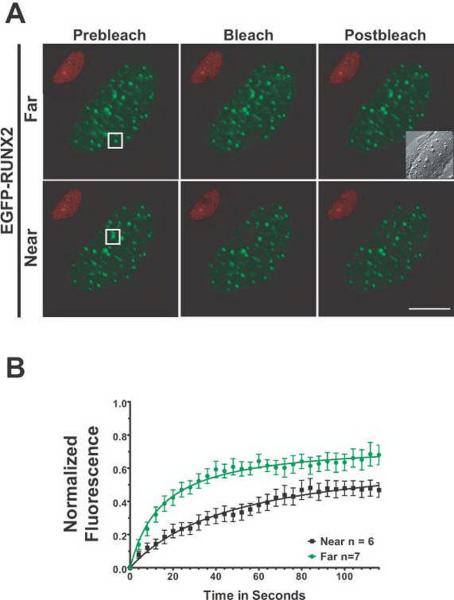
Fig. 6. RUNX2 has different binding kinetics at nucleolar versus subnuclear foci as measured by FRAP.
(A) The micrographs show the region of interest in cells before photobleaching, just after photobleaching, and 126 seconds later when the fluorescence had recovered. The size bar is 10 μm. (B) Normalized mean fluorescence recovery curves over time were calculated for RUNX2 foci at nucleoli and at subnuclear foci; the means were plotted with standard errors for each time point. Nucleolar RUNX2 foci recovered more slowly (29 seconds) and had a larger tightly bound immobile fraction (47%) than RUNX2 subnuclear foci (12 seconds, 35%). These results indicate a much stronger interaction of nucleolar RUNX2 with its binding site or partner proteins than the subnuclear RUNX2 foci.