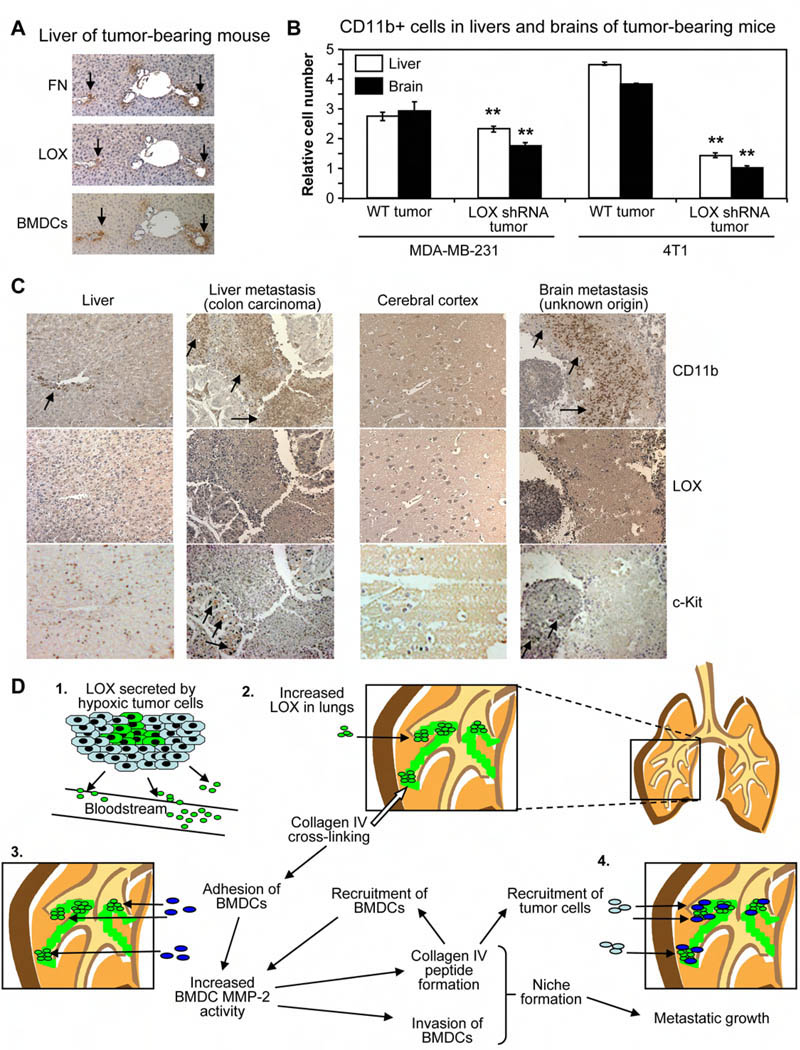
Figure 4. CD11b+ cells and LOX are associated with liver and brain metastases in patients.
(A) Serial sections from liver tissue of Wt tumor-bearing mouse stained for fibronectin, LOX, and BMDCs. Scale bar = 50µm.
(B) Flow cytometry analysis for CD11b+ cells in livers and brains of Nude mice bearing MDA-MB-231 human breast tumors or Balb/c mice with 4T1 murine mammary tumors. Data are mean ± SEM. ** = p<0.05 relative to Wt tumor-bearing mice.
(C) Tissue microarrays (TMAs) of clinical metastases stained for CD11b+ cells, LOX, or c-Kit+ cells. Samples from normal cerebral cortex and liver are provided as negative controls. Metastatic and normal TMAs were stained simultaneously, and were photographed with identical microscope and camera settings. Arrows indicate regions of CD11b+ cells or c-Kit+ cells. Scale bar = 150µm.
(D) (1) Hypoxic primary tumor cells secrete LOX into the bloodstream. (2) LOX accumulates in the lungs of tumor-bearing mice and cross-links collagen IV. (3) Adhesion of CD11b+ cells to cross-linked matrix increases BMDC MMP-2 activity. Collagen IV remodeling by LOX and MMP-2 leads to peptide formation, invasion of CD11b+ cells, and increased recruitment of BMDCs. (4) LOX-dependent formation of the pre-metastatic niche enhances metastatic growth.