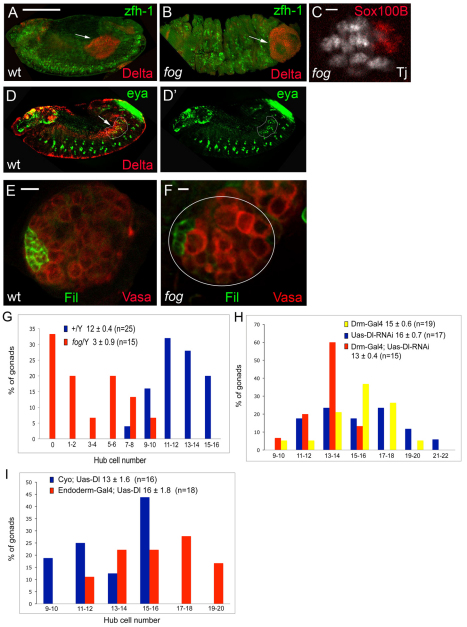
Fig. 6.
The posterior midgut (PMG) is necessary for proper hub cell specification. (A,B) Lateral view of a z-section through stage 12 male embryos from (A) wild type and (B) fog showing Delta (red, PMG; arrows) and zfh-1 (green, somatic cells). In the fog mutant (B), the PMG develops on the exterior of the embryo. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) Stage 16 fog mutant male embryo showing Sox100B (red, msSGPs) and Traffic jam (white, SGPs). Scale bar: 10 μm. (D,D′) Lateral view of a z-slice through a stage 12 wild-type male embryo showing Delta (red, PMG; arrows) and eyes absent (green, SGPs; encircled in white). z-slice: 0.7 μm. Scale bar (in A): 100 μm. (E,F) 1st larval instar male gonads from +/Y (E) and fog/Y (F). Filamin (green, hub cells) and Vasa (red, germ cells). One gonad is outlined in E; a second lies just up and to the right. Fewer germ cells contribute to the fog/Y larval gonad. Scale bars: 10 μm in D; 5 μm in E. (G) Distribution of the number of hub cells in +/Y (blue) and fog/Y (red) is shown (P<0.0001). The average number of hub cells per gonad ±s.e.m. and the number of gonads (n) observed is also shown. (H) Distribution of the number of Filamin-positive hub cells in Uas-Dl-RNAi (blue), Drm-Gal4 (yellow) and Drm-Gal4; Uas-Dl-RNAi (red) gonads is shown. Note the decreased hub cell number in Drm-Gal4; Uas-Dl-RNAi gonads (P<0.05) compared with controls, Drm-Gal4 and Uas-Dl-RNAi gonads. The average number of hub cells per gonad (±s.e.m.) and the number of gonads (n) observed is also shown. (I) Distribution of the number of hub cells in cyo;Uas-Dl (blue) and Endoderm-Gal4;Uas-Dl (red) is shown (P<0.005). The average number of hub cells per gonad (±s.e.m.) and the number of gonads (n) observed is also shown.