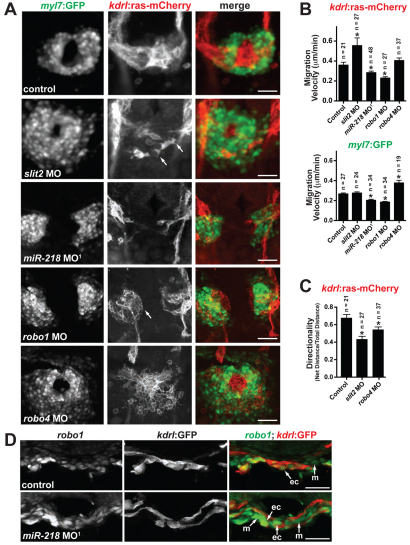
Fig. 3.
Slit/Robo signaling regulates heart tube formation. (A) Early heart field migration defects in zebrafish morphants: slit2, miR-218, robo1 and robo4. Shown is Tg(kdrl:ras-mCherry);Tg(myl7:GFP) expression at 20 somites. Dorsal views, anterior to the top. slit2 morphants have disrupted endocardial migration, including loss of sheet-like migration and endocardial cells have multiple filopodial protrusions (arrows). miR-218 and robo1 morphants have delayed migration of the endocardium and myocardium. The endocardial cells of robo1 morphants display a rounded phenotype (arrow). Migration of the heart fields is not delayed in robo4 morphants, but the morphology of the endocardial and myocardial cells is altered compared with controls. (B) Migration velocities of endocardial [Tg(kdrl:ras-mCherry) expression] and myocardial [Tg(myl7:GFP) expression] cells were quantified from time-lapse images. The number of cells tracked is shown above each bar. slit2 morphants have enhanced endocardial migration rates, whereas miR-218 and robo1 have reduced endocardial and myocardial migration rates. *, P<0.05 compared with control. (C) Directionality of migration was assessed by quantifying the ratio of the net distance traveled to the total distance traveled. A decrease in the ratio indicates an increase in the randomness of migration. slit2 and robo4 morphants have defects in directional migration. *, P<0.05 compared with control. Data in B and C are mean + s.e.m. (D) In situ analysis of robo1 expression at the 20-somite stage reveals an increase in expression in miR-218 morphants. Transverse sections, dorsal to the top. ec, endocardium; m, myocardium. Scale bars: 50 μm in A and D.