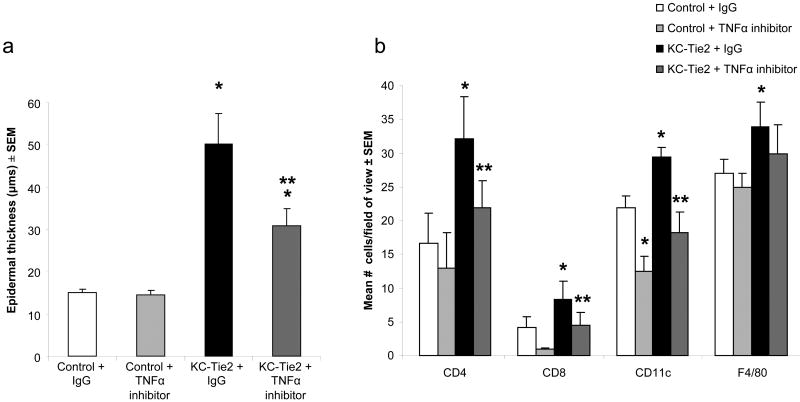
Figure 6. Systemic administration of antibodies targeting murine TNFα leads to significant improvement in the psoriasiform skin phenotype in KC-Tie2 mice.
Average epidermal thickness measures performed on H&E stained sections (a) following 4 weeks of treatment with either TNFα antibodies or IgG control demonstrates increased acanthosis in KC-Tie2 + IgG skin compared to control skin treated with either IgG or TNFα antibodies. Epidermal thickness in KC-Tie2 mice treated with TNFα antibodies is significantly decreased compared to KC-Tie2 + IgG animals, but remains thicker than control animals. TNFα antibody treatment results in a return of T cell and APC numbers back to control mouse levels. * p≤0.05 compared to control + IgG; ** p≤0.05 compared to KC-Tie2 + IgG.