Figure 3. Ethanol consumption is reduced in Cx36 KO mice in the drink-in-the-dark procedure.
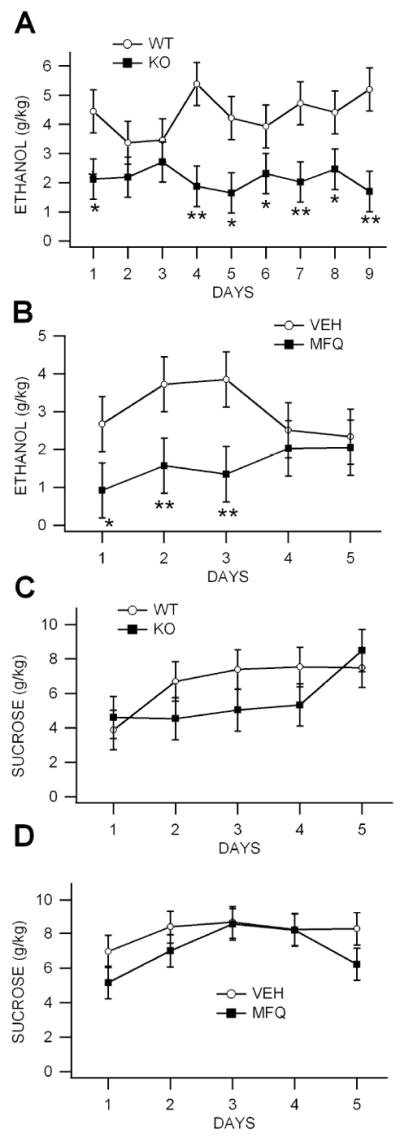
(A) Mice were allowed ad libitum access to a sipper tube containing 20% ethanol that was placed in their home cage for 2 hours 2 hours after the start of their dark phase. Knock-out mice consumed significantly less ethanol than WT mice from DAYS 1-9. (B) Wild-type mice were treated with 40 mg/kg MFQ 3 hours before testing each day. Mefloquine-treated mice consumed significantly less ethanol than vehicle (VEH)-treated WT controls. (C,D) To control for potential deficits in performance, mice were allowed ad libitum access to a sipper tube containing 10% sucrose. There was no significant difference in sucrose consumption between KO and WT mice (C) or between MFQ vs VEH WT controls (D).
