Abstract
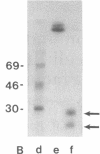
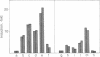
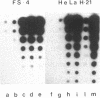
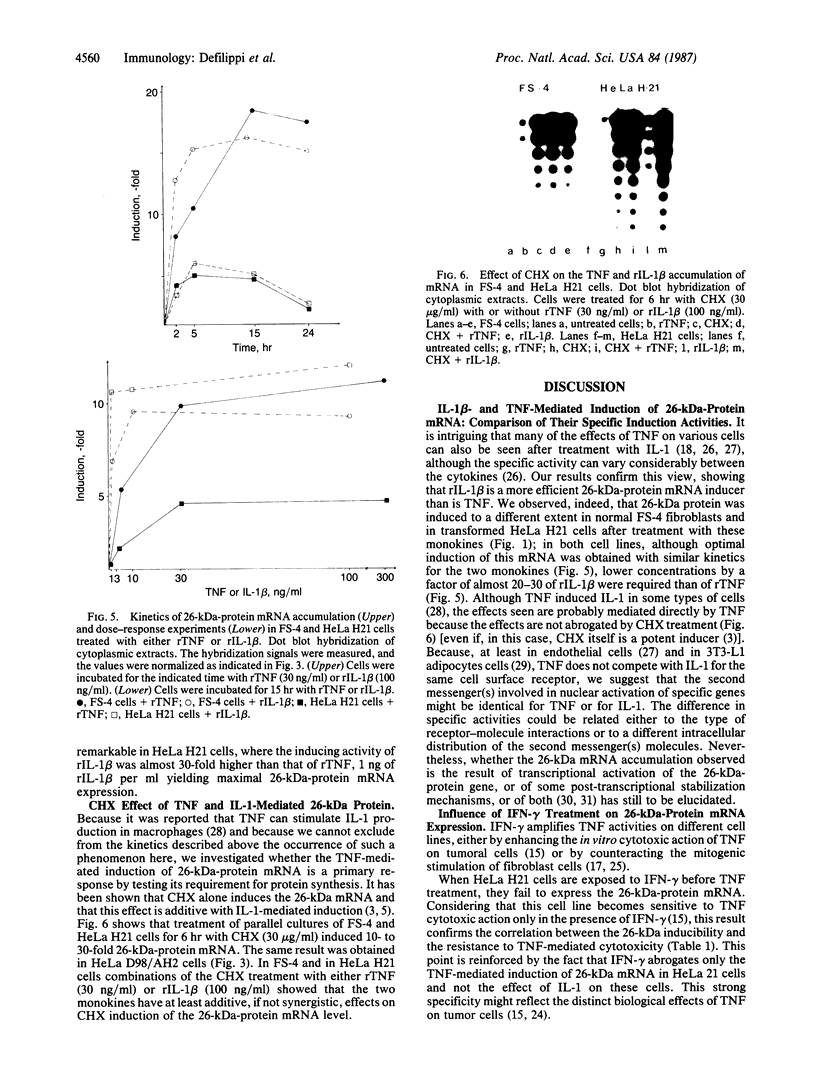
A 26-kDa protein, originally described in human fibroblasts superinduced for interferon beta (IFN-beta) production, and termed IFN-beta 2 by other investigators, is induced by cycloheximide and by a 22-kDa, interleukin 1 (IL-1)-related factor. Although the structure and sequence of the corresponding gene show nonhomology with the IFN-beta gene, the gene is identical to that of B-cell stimulatory factor 2, a human interleukin, and displays a very potent growth and differentiation factor activity for B lymphocytes. In this work we show that IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) strongly induce the 26-kDa protein in FS-4 fibroblasts and in some transformed cell lines. Addition of cycloheximide to recombinant (r)IL-1 beta and rTNF further enhances the level of 26-kDa-protein mRNA. We determined the kinetics of induction and the amounts of rTNF and rIL-1 beta required for optimal induction of this mRNA in FS-4 cells and in HeLa H21 cells and found that rIL-1 beta is a more efficient inducer of 26-kDa protein mRNA than is TNF. By analyzing the inducibility of the 26-kDa protein gene by rTNF and rIL-1 beta in a series of transformed cell lines that differ in their sensitivity to the cytotoxic action of TNF, we report a direct correlation between the 26-kDa protein mRNA expression and the resistance of these cells to the cytotoxic effect of TNF.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amasino R. M. Acceleration of nucleic acid hybridization rate by polyethylene glycol. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachwich P. R., Chensue S. W., Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates interleukin-1 and prostaglandin E2 production in resting macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):94–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90881-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. A., Cerami A. Recombinant interleukin 1 suppresses lipoprotein lipase activity in 3T3-L1 cells. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3969–3971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., De Wit L., Pierard D., Derynck R., De Clercq E., Fiers W. Secretory proteins induced in human fibroblasts under conditions used for the production of interferon beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2768–2772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., De Wit L., Poupart P., Opdenakker G., Van Damme J., Billiau A. Induction of a 26-kDa-protein mRNA in human cells treated with an interleukin-1-related, leukocyte-derived factor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):253–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Van der Heyden J., Ruysschaert R., Fiers W. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor: its effect and its synergism with interferon-gamma on a variety of normal and transformed human cell lines. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1986 Apr;22(4):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(86)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., Content J., Volckaert G., Derynck R., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Structural analysis of the sequence coding for an inducible 26-kDa protein in human fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):625–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Yasukawa K., Harada H., Taga T., Watanabe Y., Matsuda T., Kashiwamura S., Nakajima K., Koyama K., Iwamatsu A. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):73–76. doi: 10.1038/324073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., Henriksen-DeStefano D., May L. T., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. Induction of beta 2-interferon by tumor necrosis factor: a homeostatic mechanism in the control of cell proliferation. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90780-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Chaudhuri A., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction by interferon. New protein(s) determine the extent and length of the induction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmenout A., Fransen L., Tavernier J., Van der Heyden J., Tizard R., Kawashima E., Shaw A., Johnson M. J., Semon D., Müller R. Molecular cloning and expression of human tumor necrosis factor and comparison with mouse tumor necrosis factor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 4;152(3):515–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Bevilacqua M. P., Mendrick D. L., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Two distinct monokines, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor, each independently induce biosynthesis and transient expression of the same antigen on the surface of cultured human vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1680–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupart P., De Wit L., Content J. Induction and regulation of the 26-kDa protein in the absence of synthesis of beta-interferon mRNA in human cells. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;143(1):15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Yarden A., Zipori D., Kimchi A. Autocrine beta-related interferon controls c-myc suppression and growth arrest during hematopoietic cell differentiation. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90857-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M. F., Kimchi A. Initial characterization of a spontaneous interferon secreted during growth and differentiation of Friend erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1472–1480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Wakefield L. M., Roche N. S., Stern D. F., Sporn M. B. Type beta transforming growth factor: a bifunctional regulator of cellular growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):119–123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scahill S. J., Devos R., Van der Heyden J., Fiers W. Expression and characterization of the product of a human immune interferon cDNA gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4654–4658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., De Ley M., Opdenakker G., Billiau A., De Somer P., Van Beeumen J. Homogeneous interferon-inducing 22K factor is related to endogenous pyrogen and interleukin-1. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):266–268. doi: 10.1038/314266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaquero C., Sanceau J., Weissenbach J., Beranger F., Falcoff R. Regulation of human gamma-interferon and beta-interferon gene expression in PHA-activated lymphocytes. J Interferon Res. 1986 Apr;6(2):161–170. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Havell E. A., Kohase M. Superinduction of interferon with metabolic inhibitors: possible mechanisms and practical applications. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A22–A29. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Palombella V. J., Henriksen-DeStefano D., Swenson C., Feinman R., Hirai M., Tsujimoto M. Fibroblast growth enhancing activity of tumor necrosis factor and its relationship to other polypeptide growth factors. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):632–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Creasey A. A., Ladner M. B., Lin L. S., Strickler J., Van Arsdell J. N., Yamamoto R., Mark D. F. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.3856324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Chernajovsky Y., Zeevi M., Shulman L., Soreq H., Nir U., Wallach D., Perricaudet M., Tiollais P., Revel M. Two interferon mRNAs in human fibroblasts: in vitro translation and Escherichia coli cloning studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7152–7156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells V., Mallucci L. Expression of the 2-5A system during the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jul;159(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Ruggieri R., Korn J. H., Revel M. Structure and expression of cDNA and genes for human interferon-beta-2, a distinct species inducible by growth-stimulatory cytokines. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2529–2537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zullo J. N., Cochran B. H., Huang A. S., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and double-stranded ribonucleic acids stimulate expression of the same genes in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]