Figure 4.
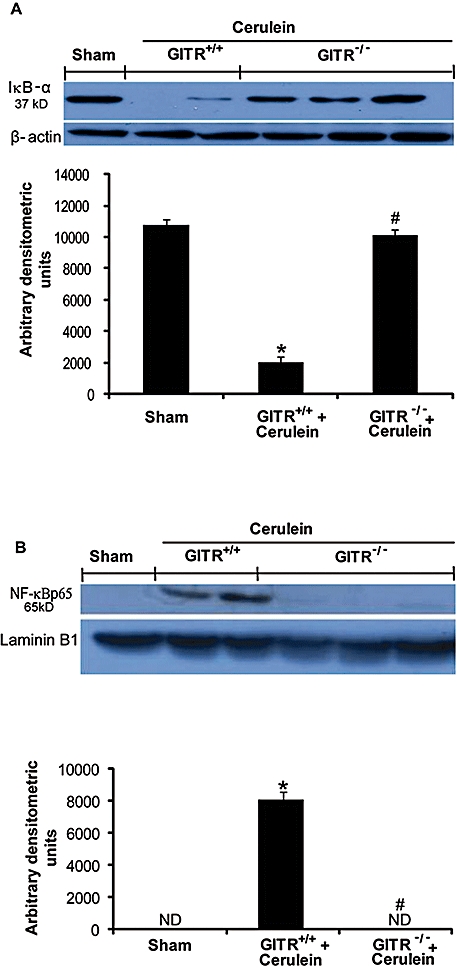
Effect of glucocorticoid-induced tumour necrosis factor receptor family-related protein (GITR) inhibition on cerulein-induced nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation in pancreas. Panels A: basal levels of inhibitor of kappa B-α (IκB-α) were detected by Western blot analysis in the homogenates of pancreatic tissues from saline-treated (sham) animals. IκB-α expression is low 24 h after cerulein administration, while it was not reduced in GITR−/− mice. β-actin was used as internal control. Panels B: levels of NF-κB p-65 subunit protein in the nuclear fractions of the pancreatic tissues were significantly increased by cerulein-administration compared to those in the sham-treated mice. The levels of NF-κB p-65 protein in the nuclear fractions of pancreatic tissues from GITR−/− mice were similar to that observed in sham-treated animals. Laminin B1 was used as internal control. Results shown in the lower half of panels A and B are expressed as mean ± SEM of the normalized densitometric analysis of five independent experiments. *P < 0.01 versus sham, #P < 0.01 versus cerulein-treated GITR+/+ mice.ND, not detectable.
