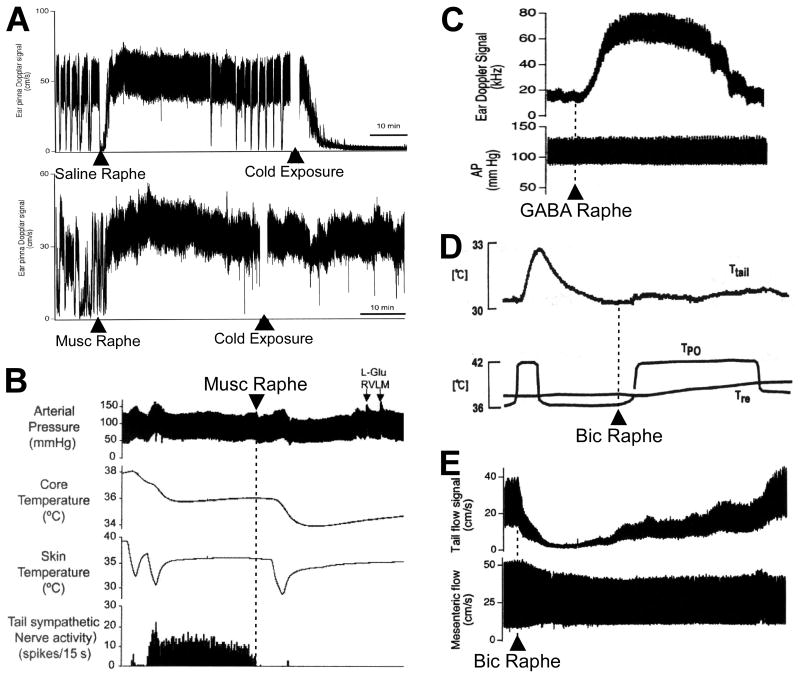
Figure 9.
Rostral medullary raphe neurons play a major excitatory role in determining cutaneous vasoconstrictor (CVC) sympathetic outflow and cutaneous blood flow. Inhibition of raphe pallidus neurons with microinjection of muscimol (Musc) or GABA prevents the cold-evoked decrease in rabbit ear pinna blood flow (A, reproduced with permission from (119)) and the cold-evoked increase in rat tail CVC activity (B, reproduced with permission from (117)) and increases rabbit ear pinna blood flow from spontaneous levels at room temperature (C, modified from (118), with permission). Increases in raphe pallidus neuronal activity following microinjection of bicuculline (Bic) prevents the increase in rat tail temperature evoked by hypothalamic warming (D, reproduced with permission from (115)) and decreases rat tail blood flow from spontaneous levels at room temperature (E, Reproduced with permission from (116)).