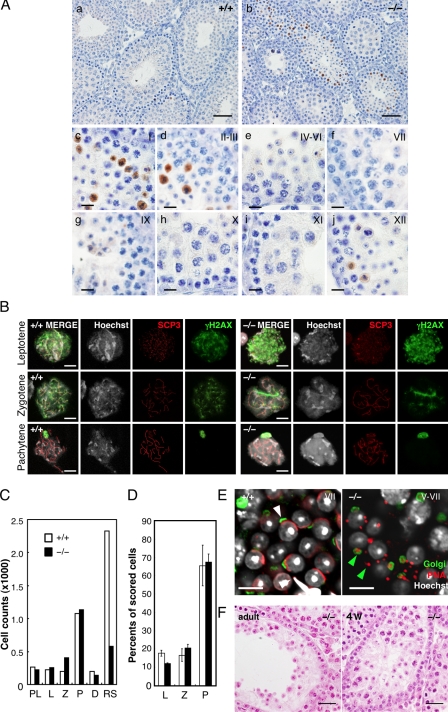
Figure 4.
Spermiogenic defects in Tdrd5−/− testes. (A) Apoptosis in Tdrd5−/− testes. Tdrd5+/+ (a) and Tdrd5−/− (b) testes stained with anti-activated Caspase3 antibody (brown) counterstained with hematoxylin. Magnified images of Tdrd5−/− seminiferous tubules at stages I (c), II and III (d), IV–VI (e), VII (f), IX (g), X (h), XI (i), and XII (j) are shown. (B) Nuclear-spread analysis of the meiotic prophase in Tdrd5+/+ (left) and Tdrd5−/− (right) testes. Meiotic spermatocytes were staged (leptotene, zygotene, and pachytene) based on the nuclear morphology (Hoechst) and the distribution pattern of SCP3 and γH2AX. The bright spots detected by γH2AX in the pachytene spermatocytes are XY bodies. (C) Total counts of the indicated cells from hematoxylin and eosin–stained sections of Tdrd5+/+ (white) and Tdrd5−/− (black) testes. PL, preleptotene; L, leptotene ; Z, zygotene; P, pachytene; D, diplotene spermatocytes; RS, round spermatids. (D) Percentage (the average with SD; error bars) of the indicated cells in the surface spreads of Tdrd5+/+ (white) and Tdrd5−/− (black) testes. (E) Acrosome visualized by PNA (red) and Golgi58K (green) staining of Tdrd5+/+ (left, white arrowhead, stage V) and Tdrd5−/− (right, green arrowheads, stage V–VII) round spermatids, counter-stained with Hoechst (white). (F) Histology of a Tdrd5−/− seminiferous tubule (left, adult; right, 4 wk old) with a severe phenotype stained by hematoxylin and eosin. Bars: (A, a and b) 50 µm; (A, c–j) 10 µm; (B and E) 10 µm; (F) 20 µm.